Overview
Understanding the key differences between kilowatts and megawatts is essential for homeowners who are concerned about their energy consumption. Kilowatts (kW) measure the energy usage of household appliances, making them relatable for individual needs. On the other hand, megawatts (MW) represent the output of large-scale power facilities, which can feel distant from our everyday lives.
It’s common to feel overwhelmed by energy bills and the complexities of energy production. However, by grasping these units, you can take meaningful steps towards managing your energy consumption more effectively.
As you explore renewable energy options, remember that kilowatts are more relevant to your personal usage, while megawatts provide insight into broader energy production contexts. This understanding empowers you to make informed decisions that align with your values and aspirations for energy independence.
Together, we can work towards a more sustainable future, ensuring that your choices not only benefit your household but also contribute positively to the environment. Let’s take this journey together, fostering a community that values both energy efficiency and renewable solutions.
Introduction
In today’s energy-conscious world, understanding the nuances between kilowatts and megawatts is essential. Many homeowners are concerned about rising energy costs and the impact on their budgets. These two units of measurement not only define how energy is consumed and produced, but they also play a critical role in optimizing energy efficiency and sustainability.
We understand that navigating these concepts can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re seeking renewable solutions. How can a clearer understanding of kilowatts versus megawatts empower you to make informed decisions about your energy consumption? Together, we can explore how this knowledge contributes to a greener future and helps you achieve energy independence.
By grasping the practical implications of these measurements, you can take meaningful steps towards reducing your energy bills and embracing sustainable practices. Let’s work towards a future where energy is not just a cost, but a source of empowerment for you and your community.
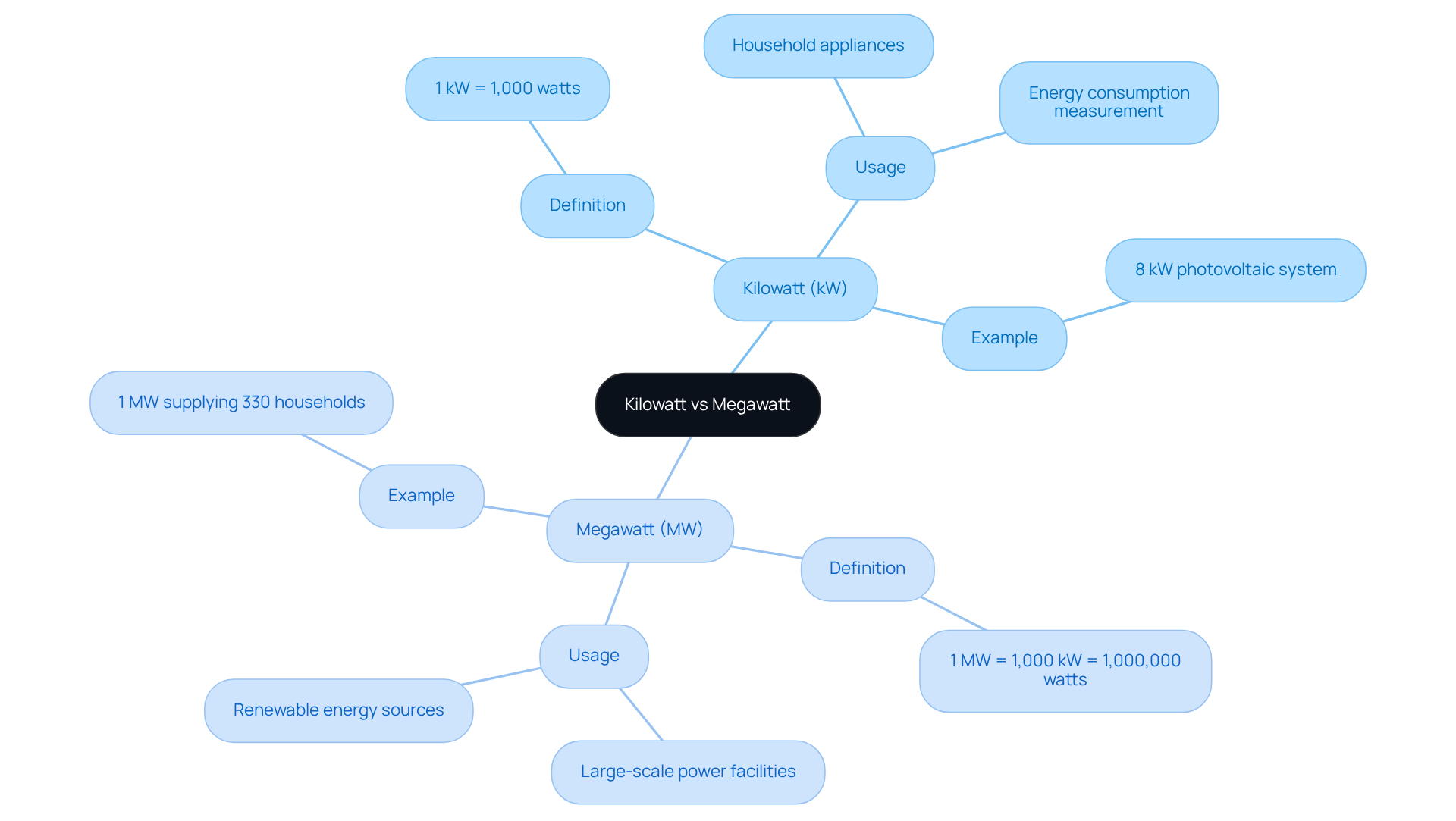
Define Kilowatt and Megawatt: Core Concepts
As a homeowner, you might find yourself concerned about rising energy bills and the impact of your energy consumption. Understanding the units of energy, particularly the differences between kilowatt vs megawatt, can be a vital step in managing these concerns.
- A kilowatt (kW), which equals 1,000 watts, is often used to measure the energy consumption of household appliances and smaller systems, especially in comparisons of kilowatt vs megawatt.
- For instance, a standard home photovoltaic panel system rated at 8,000 watts is expressed as 8 kW.
- In contrast, when discussing kilowatt vs megawatt, a megawatt (MW) represents a larger unit of energy, equivalent to 1,000 kilowatts or 1 million watts.
- Megawatts are commonly used to indicate the output of large-scale power facilities and renewable sources, like photovoltaic farms, where one megawatt can supply power to about 330 households for one hour.
We understand that navigating these definitions can feel overwhelming, but they are crucial as you explore efficiency and generation alternatives.
- For example, did you know that a typical air conditioning unit can use almost 30 kWh each day during the summer?
- Recognizing this can empower you to evaluate your power requirements and make informed decisions regarding solar power systems.
As energy experts emphasize, understanding kilowatt vs megawatt differences is vital for optimizing energy use and transitioning to sustainable practices. Together, we can work towards a future where your energy needs are met sustainably, allowing you to feel confident and supported in your choices.
Explore Applications: Kilowatts vs. Megawatts in Practice
We understand that managing energy bills can be a significant concern for homeowners. Kilowatts (kW) are primarily used in home environments to measure the energy consumption of household devices like refrigerators, air conditioners, and electric vehicles, which is often contrasted in discussions of kilowatt vs megawatt. For instance, a typical home may feature a panel system rated at 5 kW, indicating its maximum power output under ideal conditions. By understanding how their panel systems align with the 200% guideline, property owners can benefit from enhanced power production and potential savings on utility expenses.
In contrast, when discussing kilowatt vs megawatt, megawatts (MW) are utilized in larger contexts, such as assessing the output of utility-scale renewable energy farms or wind turbines. Imagine a photovoltaic facility with a capacity of 10 MW—it can supply approximately 2,000 typical households each day, significantly supporting local electricity needs. Grasping the differences between kilowatt vs megawatt is essential for consumers aiming to make informed decisions regarding energy consumption and production.
Significantly, utility-scale photovoltaic power, which boasts a total capacity of nearly 236 GW nationwide, stands as the third-largest source of renewable resources in the U.S. It supplies power to around 22 million homes and helps prevent 125 million metric tons of CO2 emissions each year. This highlights the importance of megawatt-scale installations in addressing power usage and promoting sustainability.
Furthermore, we encourage homeowners to explore complementary solutions, such as Tesla home chargers, panel cleaning services, and efficient battery options. Together, we can maximize energy efficiency and sustainability efforts, paving the way for a brighter, more sustainable future. Let’s work towards a more energy-independent tomorrow, where you can feel empowered in your choices.
Convert Energy Measurements: Understanding Kilowatt to Megawatt Transitions
We understand that managing energy bills can be a significant concern for homeowners. Understanding the difference in energy production between kilowatt vs megawatt is straightforward and can help you better comprehend your energy output. Simply divide the kilowatt value by 1,000. For instance, if a photovoltaic panel system produces 3,000 kW, it corresponds to 3 MW (3,000 kW ÷ 1,000), illustrating the difference between kilowatt vs megawatt. Conversely, in the context of kilowatt vs megawatt, to convert megawatts to kilowatts, multiply the megawatt value by 1,000. Thus, a 2 MW photovoltaic farm generates 2,000 kW (2 MW × 1,000), highlighting the distinction between kilowatt vs megawatt.
These conversions are crucial, as they enable a better comprehension of power production and consumption when considering kilowatt vs megawatt across various contexts. It’s common to feel overwhelmed by these numbers, but understanding that 1 MW can supply energy for between 400 to 900 households each year can assist you in assessing the impact of your energy systems.
Furthermore, with an average solar panel system generating approximately 10 MW annually, you can calculate potential earnings from solar renewable resources credits (SRECs), which can vary from $500 to $750. Comprehending these metrics not only assists in resource management but also supports informed choices concerning efficiency and sustainability. Together, we can work towards a more sustainable future, ensuring that your energy choices align with your values and financial goals.
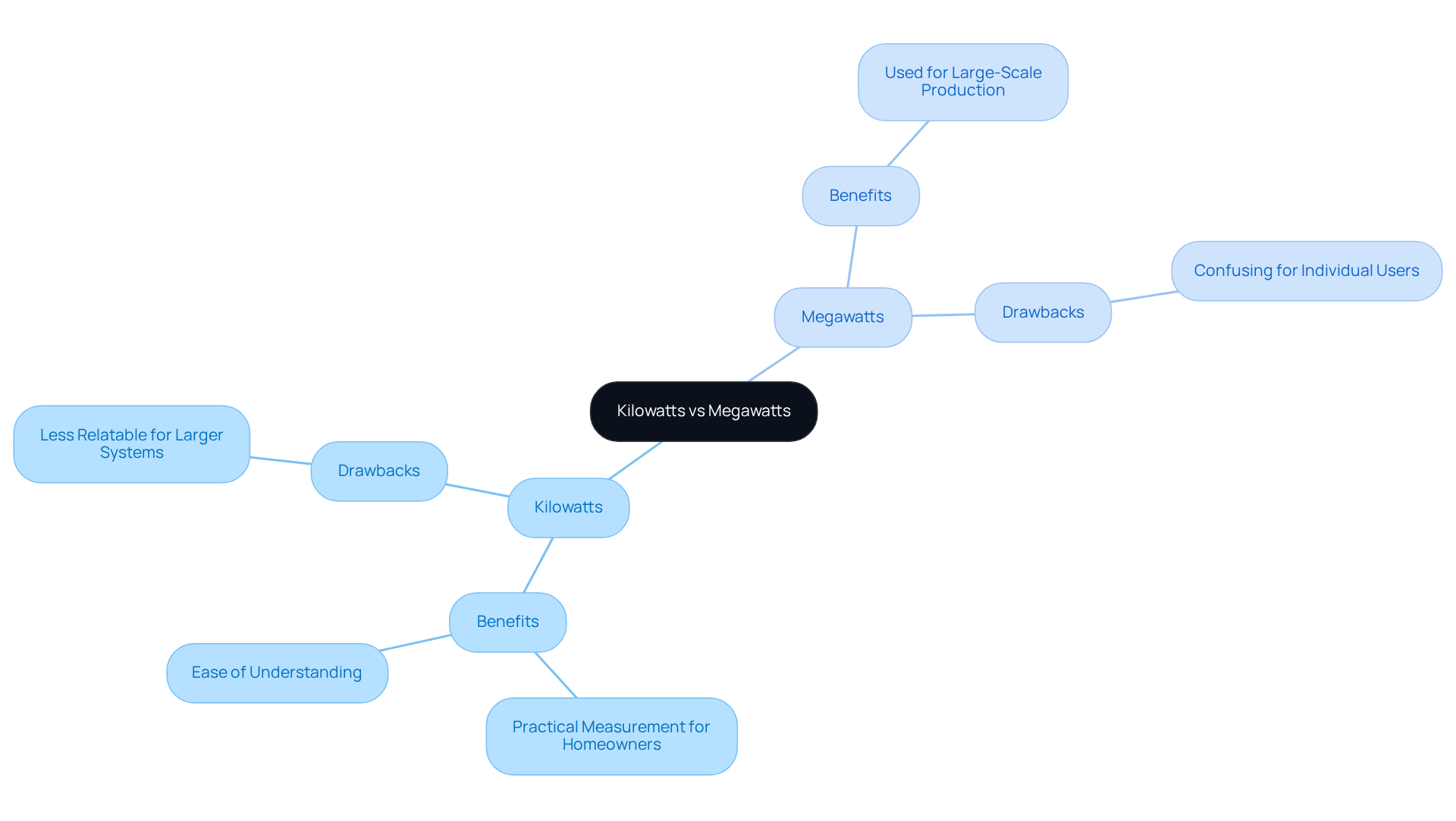
Compare Benefits and Drawbacks: Choosing Between Kilowatts and Megawatts
We understand that managing energy bills can be a significant concern for homeowners. Kilowatts serve as a practical measurement for residential applications, providing a straightforward way to gauge the power consumption of individual appliances, especially when considering kilowatt vs megawatt. This clarity not only helps in effective power management but also empowers you to make informed choices about your consumption. In the realm of solar power solutions, comprehending kilowatts is essential for those using solar panels and Tesla home chargers; it aids you in tracking usage and enhancing your systems for greater effectiveness.
However, it’s common to feel that kilowatt vs megawatt measurements may not fully depict the power needs of larger systems, where greater units become more relevant. While units of power are crucial for large-scale electricity production, they can be less relatable for individual users. For instance, many homeowners find it simpler to understand their power usage when comparing kilowatt vs megawatt, while utility firms frequently announce power generation in megawatts. This discrepancy can lead to confusion when evaluating power requirements and expenses.
Furthermore, consultants mention that the use of various units can obscure the specific power requirements of individual households, making it challenging for you to connect with your usage patterns. Ultimately, the decision between kilowatt vs megawatt hinges on the context of energy use and generation. By focusing on kilowatts for personal energy management, you can better navigate your energy needs, especially when considering the economic and environmental benefits of solar energy systems. Together, we can work towards a more sustainable and energy-independent future.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between kilowatts and megawatts is crucial for homeowners concerned about managing their energy consumption effectively. These units not only represent different scales of energy measurement but also serve practical purposes in everyday life, from household appliances to large-scale energy production. By recognizing how kilowatts apply to personal energy use while megawatts reflect broader energy generation, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions that align with your financial and environmental goals.
We understand that energy bills can be a source of stress, and throughout this article, we highlighted key insights, such as the significance of kilowatts in residential settings for tracking energy use and the role of megawatts in assessing the output of renewable energy sources. The ability to convert between these measurements further facilitates a better understanding of energy dynamics, enabling you to optimize your systems for efficiency and sustainability. Moreover, being aware of your energy consumption patterns allows you to make conscious choices that promote both economic and ecological benefits.
Ultimately, embracing knowledge about kilowatts and megawatts is more than just an academic exercise; it is a pathway to energy independence and sustainability. By taking proactive steps to understand and manage your energy usage, you can contribute to a greener future while alleviating financial burdens. Engaging with renewable energy solutions and optimizing energy consumption not only benefits your personal budget but also supports broader environmental goals, fostering a community committed to sustainable practices. Together, let’s work towards a brighter, more sustainable future.


