Overview
In today’s world, many homeowners are understandably concerned about rising energy bills. The article highlights the key differences between watts and kilowatts, shedding light on their significance for eco-conscious individuals who are striving to manage their energy consumption and costs effectively.
- While watts measure the power usage of individual devices,
- kilowatts are applied to larger appliances and systems.
This distinction empowers homeowners to make informed decisions that can enhance energy efficiency and ultimately reduce utility expenses. By understanding these concepts, we can work together towards a more sustainable future, ensuring that our homes not only meet our needs but also reflect our commitment to the environment.
Introduction
We understand that managing energy consumption and costs is a top concern for homeowners today. As energy bills continue to rise and environmental worries become more pressing, grasping the nuances between watts and kilowatts is not just beneficial—it’s essential. By understanding these fundamental power units, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions about your electricity usage, ultimately leading to significant savings and a more sustainable lifestyle.
It’s common to feel overwhelmed by the complexity of energy measurements, but navigating the differences between watts and kilowatts can enhance your efficiency and reduce expenses. This article delves into the critical distinctions between these two units, providing insights that can guide you toward energy independence. Together, we can explore how this knowledge can lead to a brighter, more sustainable future for your home.
Define Watts and Kilowatts: Understanding the Basics
As homeowners, we often find ourselves concerned about rising energy bills and the impact they have on our budgets. Understanding the basics of power units, such as the , can be a crucial step in addressing these concerns.
- Watts (W) are the fundamental unit of power in the International System of Units (SI), representing the rate at which energy is used or produced. To put it simply, one unit of power is defined as one joule per second.
- When we compare watts versus kilowatts (kW), we find that a kilowatt is a larger unit of power, with one kilowatt equaling 1,000 watts.
- This distinction regarding watts versus kilowatts is particularly important when assessing the power needs of various devices and systems, such as photovoltaic panels, power storage solutions, and Level 3 chargers for electric vehicles.
By grasping these units, we can take the first step towards enhancing our energy consumption and lowering expenses in our homes. This is especially true for those of us who are environmentally conscious and eager to adopt energy-efficient devices and explore alternative energy solutions.
Together, we can work towards a more sustainable future, where energy independence is within reach. It’s common to feel overwhelmed by the choices available, but remember, understanding your power needs is a powerful first step in making informed decisions that can lead to significant savings and a positive impact on the environment. Let’s embrace this journey towards energy efficiency together.
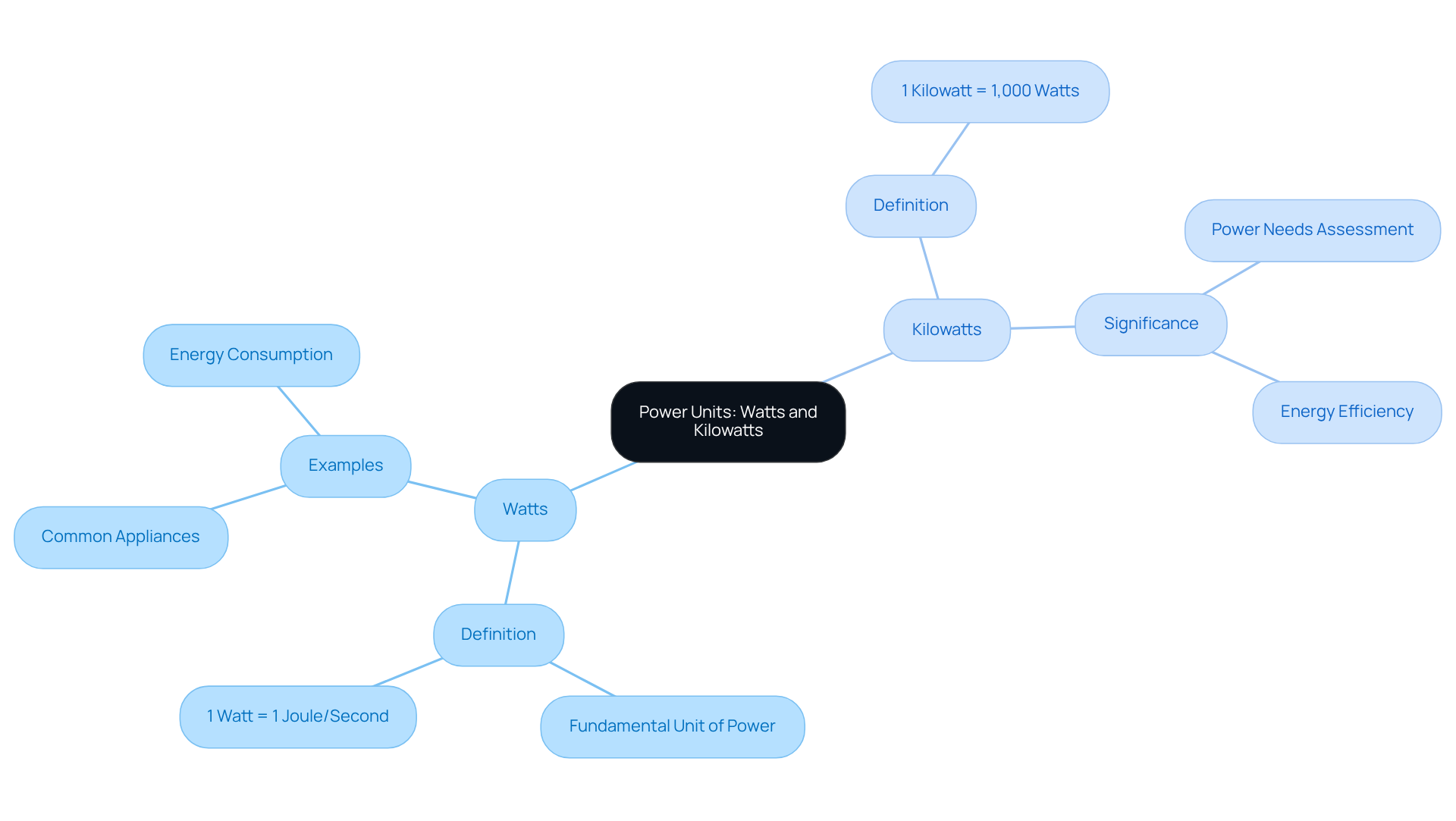
Explore Practical Applications: When to Use Watts vs. Kilowatts
As homeowners, we often find ourselves concerned about the rising costs of energy bills. It’s common to feel overwhelmed by the power consumption of our everyday appliances, from light bulbs to televisions. For instance, a light bulb may consume around 60 watts, while a TV might use about 100 watts. However, when it comes to larger devices, such as air conditioners or solar panel systems, kilowatts become the standard measure. A photovoltaic panel system, for example, can be rated at 5 kW, which means it has the capacity to generate 5,000 watts of power at peak performance.
Understanding when to use watts versus kilowatts is essential for anyone aiming to enhance and explore sustainable options, especially in the context of solar water heaters. By making informed choices, we can significantly reduce our dependence on traditional power sources. Consider the power usage of various household devices:
- A central air conditioner may draw between 1,000 to 4,000 watts
- A washing machine typically operates at around 500 watts
By recognizing these distinctions, we can effectively plan our energy needs and improve our efficiency.
Together, let’s invest in energy-efficient appliances and solar heating systems. Not only do these choices reduce our energy consumption, but they also lead to substantial savings over time, benefiting both our wallets and the environment. By embracing these sustainable solutions, we can work towards a brighter, more energy-independent future. If you have questions or need guidance, we’re here to support you on this journey.
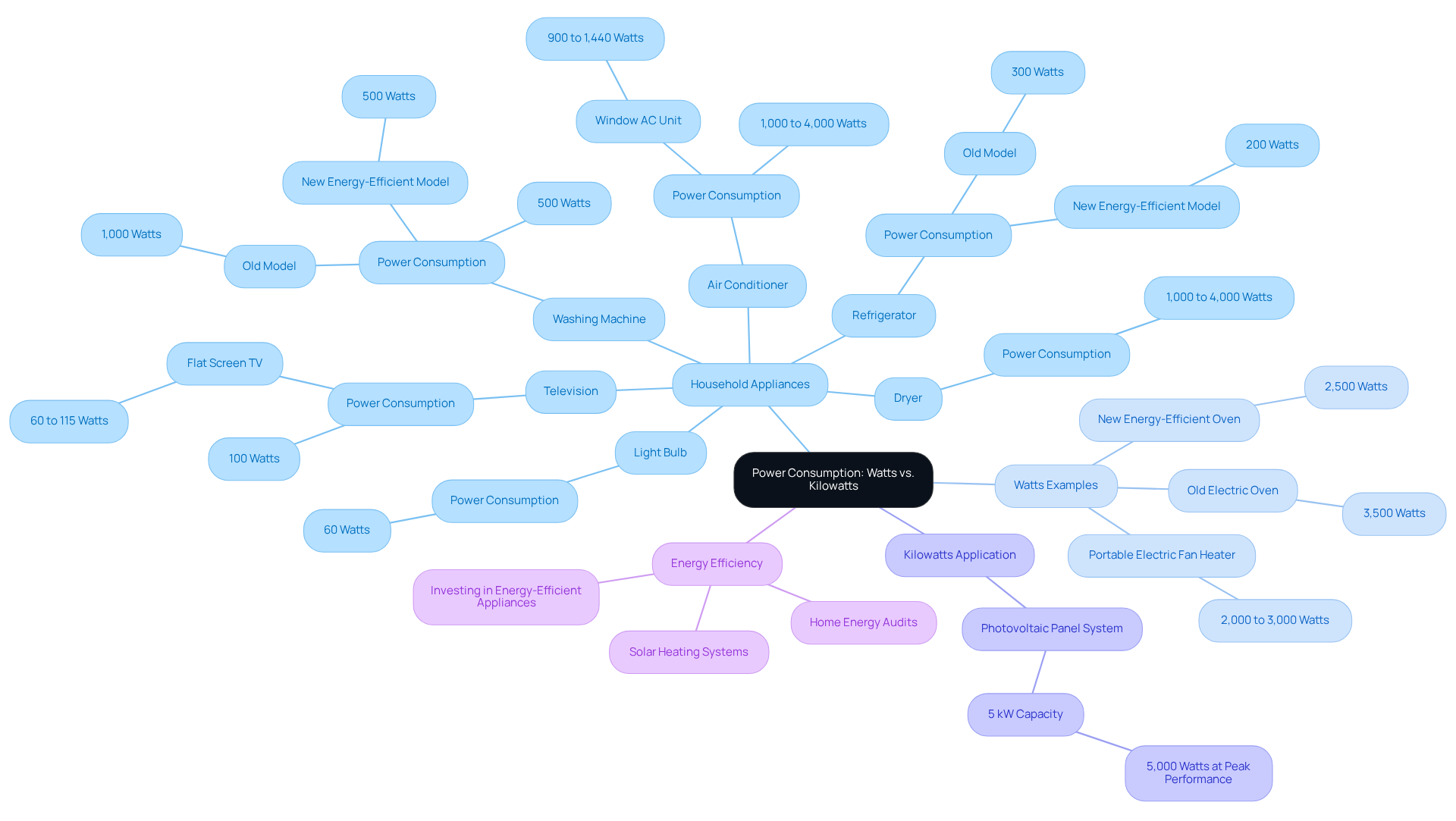
Analyze Energy Costs: Impact of Watts and Kilowatts on Your Bill
We understand that can be overwhelming, especially when they’re determined by kilowatt-hours (kWh), which measure the total power used over time. For instance, a 1,000-watt device operating for one hour uses 1 kWh of power. This understanding is crucial for property owners who are looking to control their utility expenses efficiently. By transforming watts versus kilowatts and then into kilowatt-hours, residents can assess their monthly usage and uncover potential savings, particularly when considering renewable energy options.
Imagine if a household consumes 800 kWh monthly; they can calculate their costs based on their utility’s rate per kWh, which in California averages around 32.41 cents. This computation allows property owners to evaluate the financial benefits of switching to renewable sources, where they could save as much as 40% on their electricity expenses. Additionally, investing in solar energy can lead to significant long-term savings. For example, a $100 monthly electric bill could accumulate to over $93,000 in 30 years without solar.
By grasping these metrics, property owners can make informed decisions that enhance their autonomy and reduce overall expenses. Together, we can explore these options and work towards a more sustainable future, ensuring that you feel supported every step of the way.
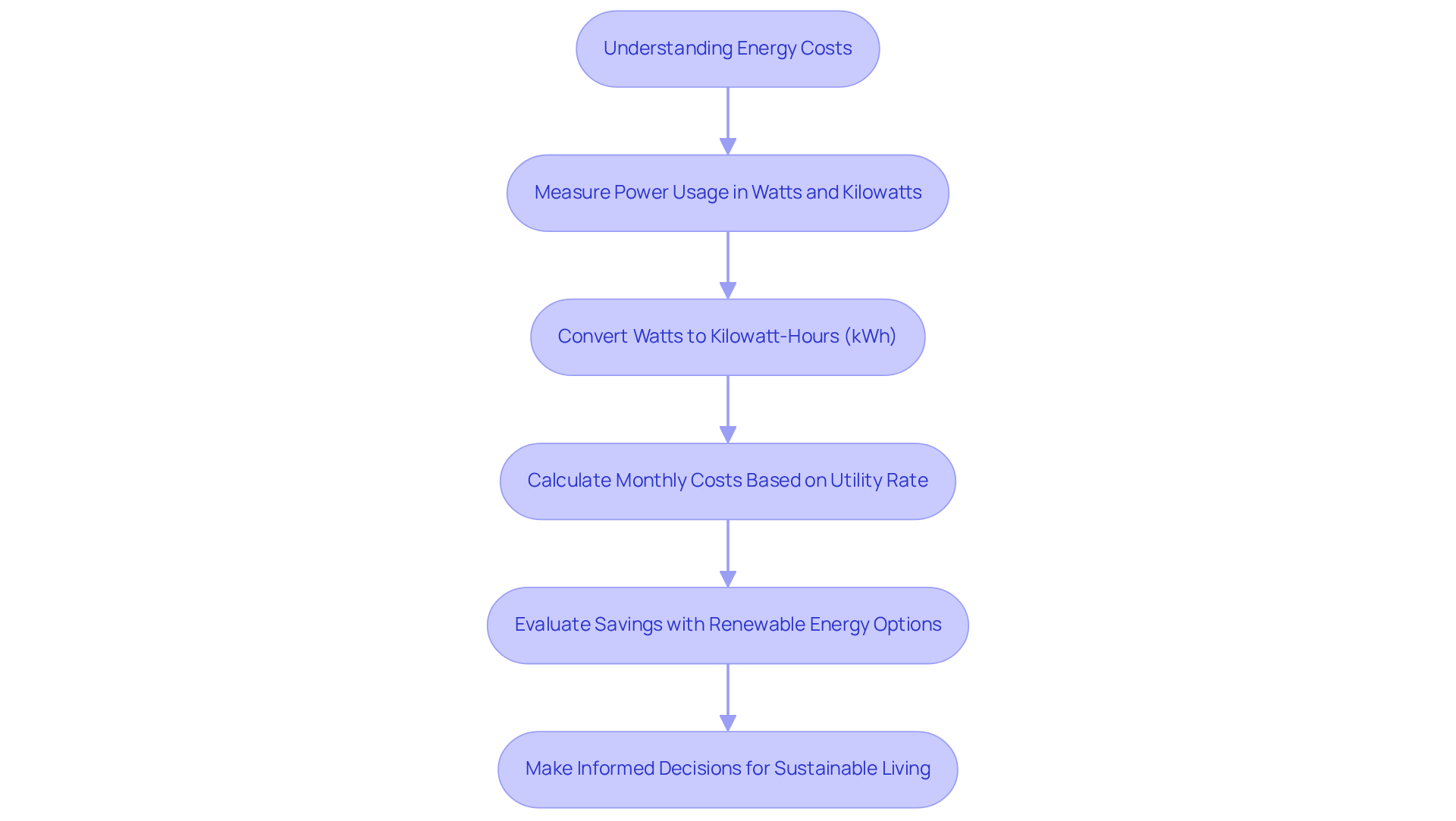
Compare Advantages and Disadvantages: Watts vs. Kilowatts
When considering watts versus kilowatts, it’s important to understand their respective benefits and drawbacks to manage power effectively. We know that homeowners often worry about their energy bills, and watts serve as a perfect tool for assessing the power usage of individual devices. This allows you to easily identify those power-hungry appliances. For example, did you know that a refrigerator typically consumes between 0.3 to 0.8 kW, while a microwave can use between 0.6 to 1.0 kW? This detailed insight helps in recognizing which devices contribute most to your utility expenses.
However, as the power requirements of larger systems increase, the comparison of watts versus kilowatts can feel overwhelming due to the sheer size of the numbers involved. This is where watts versus kilowatts come into play, offering a more manageable number for larger appliances and systems, such as HVAC units or solar panel arrays. For instance, a single installation may need approximately 7.38 kW to meet daily power requirements. This simplification allows you to grasp overall power usage at a glance, making it easier to track your consumption.
Yet, we understand that utilizing kilowatts can be less straightforward for evaluating smaller devices, which might lead to confusion when trying to across various appliances. By comprehending both watts versus kilowatts measurements, you can more effectively manage your usage, identify opportunities for savings, and make informed decisions about your systems. This dual understanding is essential for transitioning to more sustainable power practices and reducing overall expenses.
Furthermore, consider that the average US household power consumption is around 10,632 kWh annually, underscoring the importance of these measurements in managing usage effectively. Smart thermostats can also play a significant role in optimizing power consumption, further supporting eco-conscious practices. Together, let’s work towards a more sustainable future, ensuring that your energy choices lead to both savings and a positive impact on the environment.
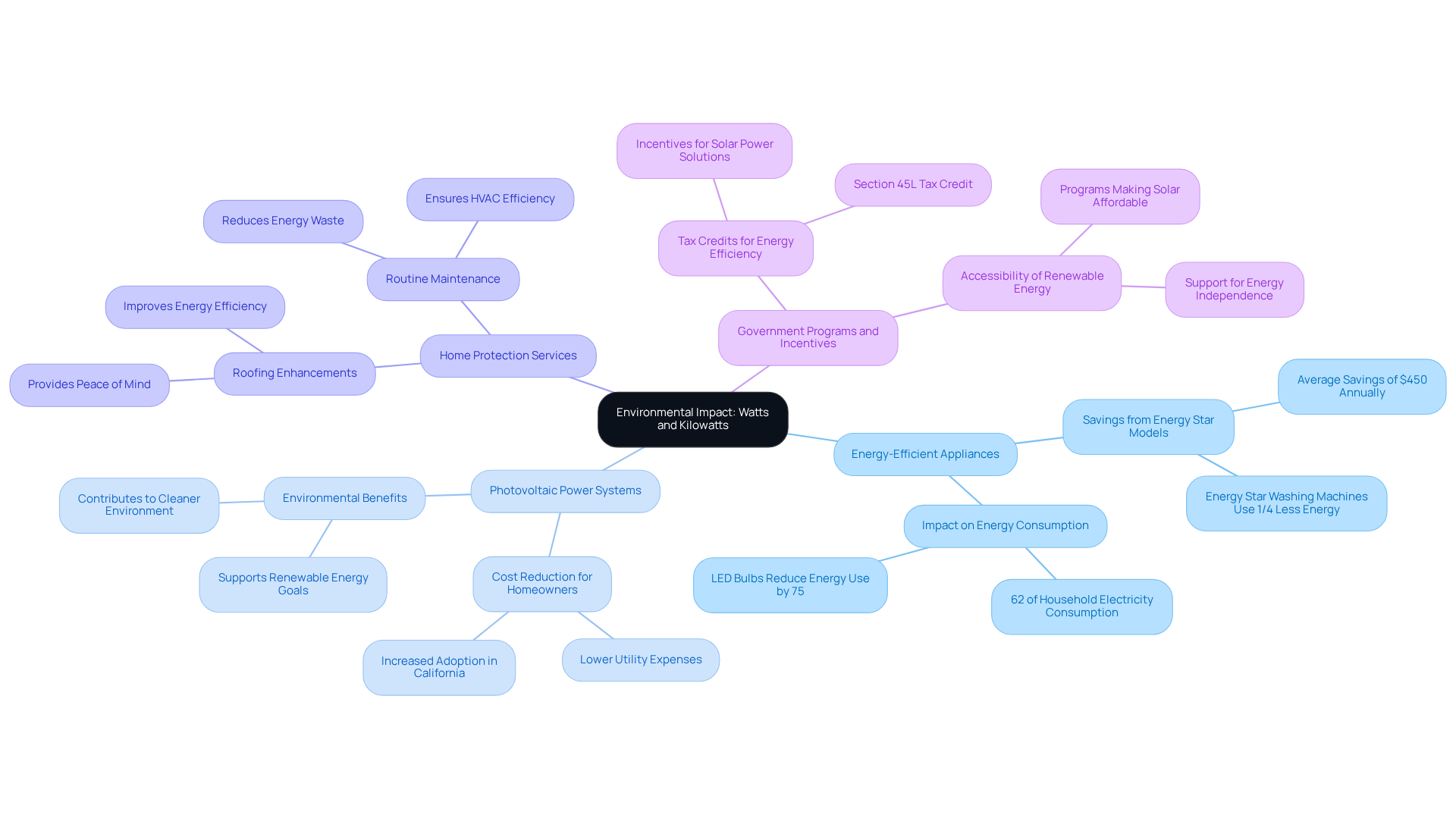
Consider Environmental Impact: Watts and Kilowatts in Sustainable Energy
The environmental impact of power usage is a significant concern for eco-conscious homeowners like you. Understanding the relationship between watts versus kilowatts is essential for making informed choices that effectively reduce carbon footprints. Here are some key considerations to reflect on:
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: By selecting appliances that consume fewer watts, you can achieve substantial reductions in overall energy consumption. Families that replace older appliances with Energy Star models can save approximately $450 each year on utility bills, which is a meaningful step towards energy independence.
- Photovoltaic Power Systems: Investing in photovoltaic power systems from Powercore Electric not only enhances your sustainability efforts but also significantly lowers your utility expenses. In California, where renewable power adoption is thriving, homeowners have the opportunity to harness sustainable resources, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Home Protection Services: Alongside cost savings, Powercore Electric offers roofing enhancements that protect your home while improving energy efficiency. It’s common to feel overwhelmed by the options, but these enhancements can provide peace of mind.
- Government Programs and Incentives: You may also benefit from various that make solar power solutions more affordable and accessible.
By prioritizing energy-efficient choices and renewable energy sources, you can create a meaningful impact on your energy consumption and environmental footprint. Together, let’s recognize the importance of understanding the distinction between watts versus kilowatts as a crucial aspect of sustainable living. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between watts and kilowatts is essential for eco-conscious homeowners who are concerned about optimizing their energy consumption and reducing costs. We recognize that by grasping these fundamental power units, you can make informed decisions that not only save you money but also contribute to a more sustainable future. It’s important to know that while watts measure the power of individual devices, kilowatts represent larger energy consumption, empowering you to better manage your electricity use.
This article highlights several key insights, including:
- The practical applications of watts and kilowatts in everyday appliances
- Their impact on energy bills
- The advantages of investing in energy-efficient solutions
By analyzing household devices and understanding their power requirements, you can identify opportunities for savings and enhance your energy efficiency. Additionally, the environmental benefits of choosing renewable energy sources and energy-efficient appliances are significant, leading to both financial savings and a reduced carbon footprint.
Ultimately, embracing the knowledge of watts versus kilowatts is a vital step toward achieving energy independence and sustainability. By making conscious choices about your energy consumption, you play a crucial role in fostering a cleaner environment. The journey toward energy efficiency is not only beneficial for your household but also contributes to a collective effort for a greener planet. Together, let’s take action today by evaluating our energy needs and exploring sustainable options that align with eco-friendly living.


