Overview
We understand that managing energy bills can be a source of concern for many homeowners. It’s essential to grasp the difference between kilowatts and watts, as this knowledge can empower you to make informed decisions about your energy consumption.
- A watt represents one joule per second.
- A kilowatt equates to 1,000 watts.
This distinction is particularly important when it comes to larger appliances that consume more energy. By understanding these measurements, you can take steps towards more efficient energy use, which can lead to significant savings on your utility bills. Together, we can work towards a more sustainable future, ensuring that your energy choices not only benefit your wallet but also promote a healthier environment.
Introduction
Understanding the nuances between kilowatts and watts is crucial for homeowners like you, who are striving to manage energy consumption and costs effectively. These power units not only quantify energy usage but also significantly impact how much you pay on your monthly utility bills. It’s common to feel overwhelmed by these distinctions, raising the question: how can a clearer understanding of these terms lead to smarter energy choices and potential savings? By exploring this topic together, we can uncover practical insights that empower you to optimize your energy use and foster a more sustainable lifestyle.
Define Watts and Kilowatts: Understanding Power Units
We understand that managing energy bills can be a significant concern for homeowners. Understanding the difference between kilowatt and watt is essential, as both are vital units that help us quantify the rate of energy utilization or generation. A watt, defined as one joule per second, signifies a small quantity of energy, while the difference between kilowatt and watt is that a kilowatt equals 1,000 watts. This distinction is crucial in recognizing the difference between kilowatt and watt, as kilowatts are typically used to indicate the output of larger electrical devices and systems, such as solar panels and household appliances.
Comprehending these units is essential for homeowners seeking to enhance their resource use and save money. For instance, typical home appliances have varying energy needs:
- A refrigerator may use around 100 to 800 watts.
- Air conditioning units can represent nearly 19% of a home’s overall energy usage.
By acknowledging these numbers, you can make informed choices about your consumption and identify opportunities for savings.
It’s common to feel overwhelmed by energy costs, but specialists highlight the importance of understanding measurement units to improve resource efficiency. A professional home power audit, for example, can uncover how much electricity is wasted by appliances in standby mode, which can significantly impact your monthly bills. Real-world examples show that individuals who actively monitor their wattage usage can modify their habits—such as turning off lights when leaving a room or upgrading to ENERGY STAR certified appliances—to reduce their electricity expenses.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between kilowatt and watt empowers you to manage your consumption effectively. Together, we can work towards more efficient usage and potential savings on your electric bills, fostering a more sustainable future for all.
Differentiate Between Watts and Kilowatts: Key Distinctions
Understanding the difference between kilowatt and watt is essential for homeowners concerned about their energy bills. Watts measure the energy consumption of smaller devices, like LED light bulbs, which typically use around 10 watts. On the other hand, kilowatts are reserved for larger appliances, such as air conditioners and solar panel systems, which can require several kilowatts of energy. For instance, a window air conditioner running continuously can consume approximately 1,320 kWh each year, highlighting how device power ratings significantly impact utility costs.
We understand that managing these energy costs is crucial for property owners, as it directly influences efficiency and potential savings. Did you know that the average American home uses about 10,791 kWh annually? Key appliances like refrigerators and dryers contribute significantly to this total. By understanding the difference between kilowatt and watt in their devices’ wattage, residents can make informed decisions about their power consumption, potentially reducing their electricity expenses.
Moreover, expert insights suggest that understanding these power units can lead to better management strategies, empowering homeowners to optimize their energy use and enhance their independence. This knowledge enables practical steps, such as investing in energy-efficient appliances or exploring solar options, ultimately leading to lower utility costs and a more sustainable lifestyle. Together, we can take meaningful steps towards a brighter, more efficient future.
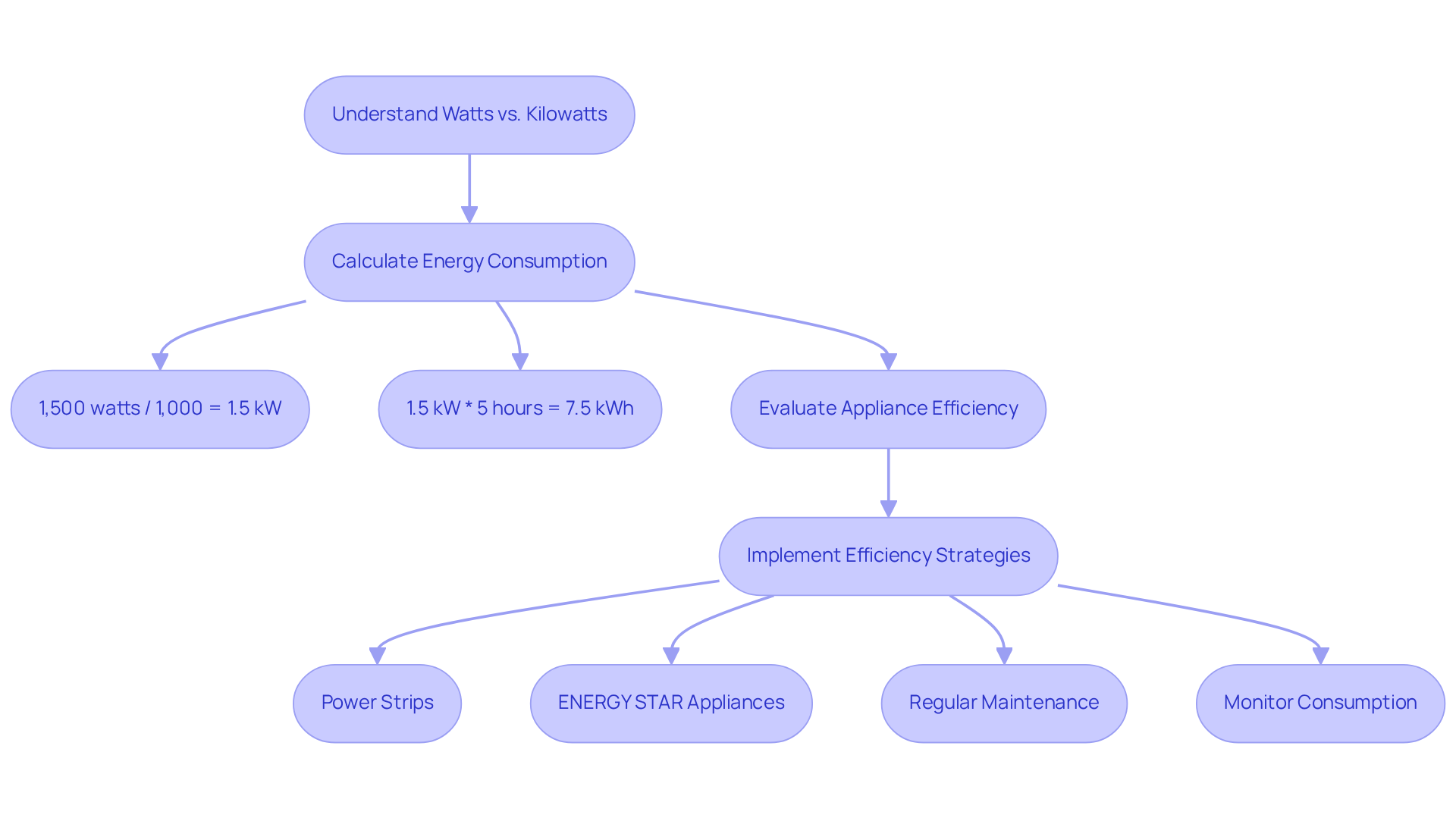
Explore Practical Applications: How Watts and Kilowatts Impact Energy Use
Understanding the difference between kilowatt and watt is crucial for homeowners who want to manage their energy consumption and expenses effectively, especially when considering solar power options. For example, a 1,500-watt electric heater running for 5 hours consumes 7.5 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of power. This calculation is straightforward:
- 1,500 watts divided by 1,000 equals 1.5 kW,
- and multiplying by the 5 hours of operation yields 7.5 kWh.
Such calculations empower homeowners to assess their power usage accurately, enabling informed decisions about efficient devices and practices.
Moreover, the impact of energy-saving devices on home utility costs cannot be overstated. Imagine switching from an old washing machine that uses around 1,000 watts to a new energy-efficient model that consumes only about 500 watts. This change can cut the power usage for that appliance by fifty percent. Not only does this adjustment lower electricity bills, but it also contributes to a more sustainable energy footprint.
Homeowners can further optimize their resource usage by adopting simple efficiency strategies based on their habits. Utilizing power strips for easy shutdown of multiple devices, upgrading to ENERGY STAR appliances, and performing regular maintenance can significantly lower utility costs. Additionally, understanding the average power usage of common household devices helps identify opportunities for savings.
Recent insights from energy consultants reveal the importance of monitoring consumption with tools like electricity usage monitors and audits. These resources provide valuable insights into power consumption trends, allowing homeowners to develop strategies to reduce usage and expenses effectively. By understanding the difference between kilowatt and watt, residents can make informed choices that enhance their energy independence and reliability, particularly when assessing solar power options tailored to their unique needs. Furthermore, case studies demonstrate how homeowners have successfully reduced their costs and improved efficiency by applying these principles, particularly under the 200% rule, which allows for the optimization of solar panel installations.
Highlight Importance: Why Knowing Watts and Kilowatts Matters for Energy Efficiency
Understanding the difference between kilowatt and watt is essential for homeowners who want to tackle rising energy bills and enhance their energy efficiency. We recognize that navigating energy usage can feel overwhelming, but by learning how different devices consume energy, you can make informed decisions that lead to significant savings. For example, switching from high-wattage appliances to energy-efficient alternatives can dramatically lower your monthly bills.
Moreover, when considering solar power systems, understanding the difference between kilowatt and watt empowers you to assess your consumption needs effectively. This ensures you choose a system that meets your requirements without overspending. This knowledge not only supports cost savings but also helps you reduce your carbon footprint, contributing to a more sustainable future.
It’s common to feel uncertain about making such changes, but statistics show that the adoption of solar energy systems has surged, with installations increasing by an average of 32% each year since 2005. By understanding your power consumption, you can take advantage of these trends, making choices that enhance both your financial and environmental well-being. Together, we can work towards a greener, more energy-independent future.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between kilowatts and watts is essential for homeowners who are concerned about managing their energy consumption and expenses effectively. These two units of measurement are crucial in quantifying energy use, with watts representing smaller appliances and kilowatts denoting larger systems. By grasping this difference, you can make informed decisions that lead to significant savings on your energy bills.
We recognize that many homeowners worry about rising energy costs. This article highlights several key insights, including:
- The varying power requirements of common household appliances
- The importance of energy-efficient practices
By monitoring energy consumption and investing in energy-saving devices, you can optimize your resource usage and reduce unnecessary expenses. Furthermore, exploring solar power options illustrates how understanding these units can empower you to choose the right systems for your needs, ultimately fostering both financial and environmental benefits.
It’s common to feel overwhelmed by energy choices, but knowledge of watts and kilowatts is not merely academic; it serves as a practical tool for enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability. By taking proactive steps to understand and manage your energy consumption, you can contribute to a greener future while enjoying the financial rewards of reduced utility costs. Together, we can embrace this knowledge as a crucial step toward achieving energy independence and making a positive impact on the environment. Let’s work towards a brighter, more sustainable future together.


