Overview
The sun is considered a renewable resource because it provides a virtually limitless supply of energy that can be harnessed through technologies like photovoltaic panels and Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems, which convert sunlight into electricity. The article supports this by detailing advancements in solar technology, the significant cost savings for users, and the environmental benefits of reducing reliance on fossil fuels, demonstrating the sun’s potential to sustainably meet energy needs indefinitely.
Introduction
As the world grapples with the urgent need for sustainable energy solutions, solar energy emerges as a beacon of hope, offering a renewable resource that is both abundant and accessible. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and harmful to the environment, solar power harnesses the sun’s rays, providing a clean and virtually limitless energy source.
With advancements in technology enhancing efficiency and affordability, more homeowners and businesses are turning to solar solutions to not only reduce their carbon footprint but also to achieve significant financial savings.
This article delves into the multifaceted benefits of solar energy, from its operational mechanics to the challenges faced by potential users, while highlighting the critical role it plays in the global transition towards a sustainable future.
Understanding Solar Energy as a Renewable Resource
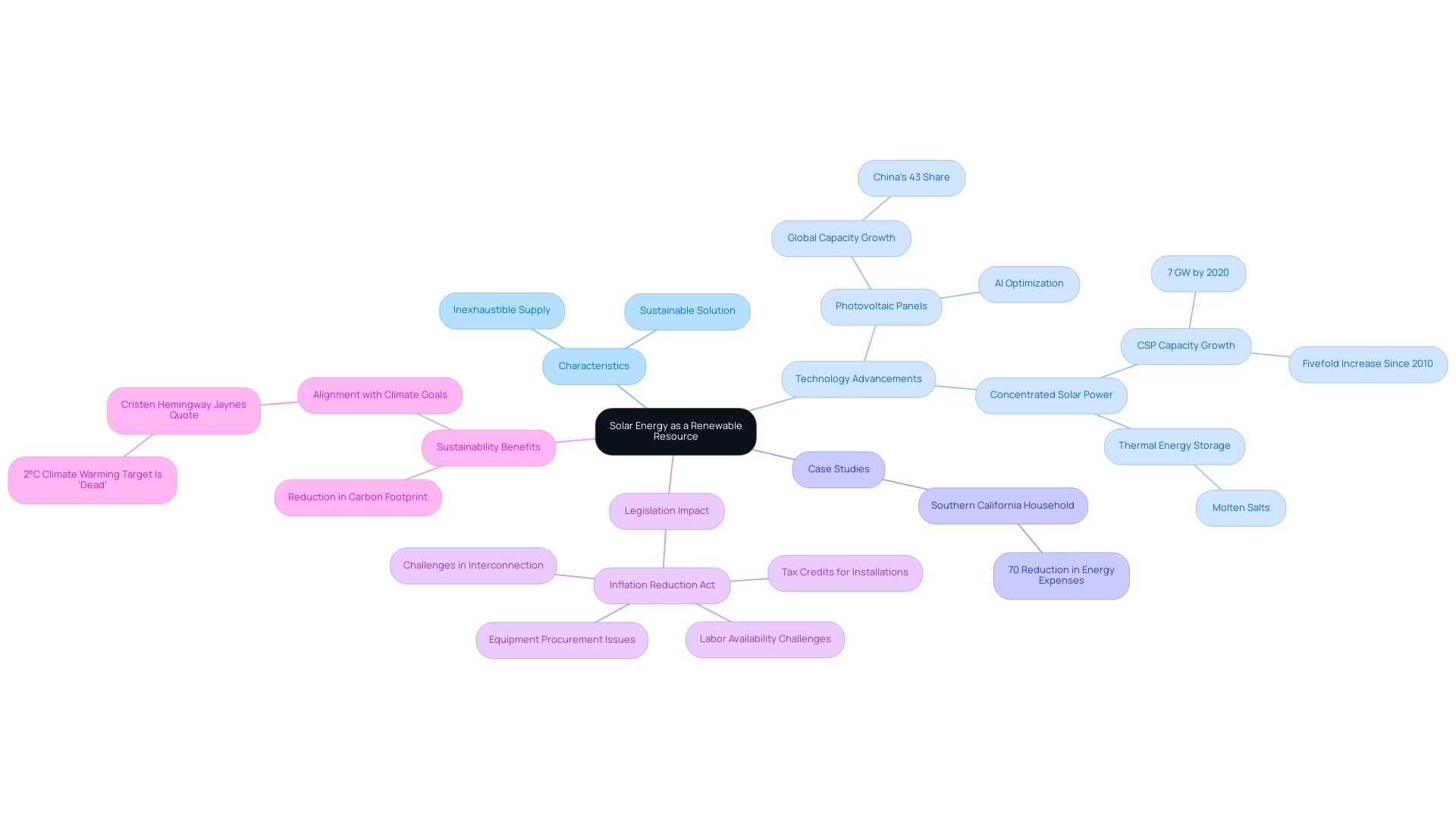
Solar power stands out as a premier renewable resource, and the question is, is sun a renewable resource derived from its inexhaustible source, which is emitted continuously and remains unexhausted by human activity. In stark contrast to fossil fuels that require millions of years to form and are subject to depletion, the fact that sunlight is sun a renewable resource provides a virtually limitless supply, available as long as the sun shines. This characteristic positions sunlight power as a sustainable solution for fulfilling the power requirements of residential and commercial sectors alike.
The most recent developments in photovoltaic panel systems have further enhanced the effectiveness of capturing sunlight, enabling increased power generation. For instance, the global photovoltaic (PV) capacity has surged, with China now accounting for an impressive 43% of this capacity. Additionally, Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) technology exemplifies the advancements in sunlight harnessing, utilizing mirrors to concentrate rays to generate electricity.
By the end of 2020, the global installed capacity of CSP reached nearly 7 GW, marking a fivefold increase since 2010. CSP systems can store thermal power using molten salts, enabling electricity generation even after sunset, which enhances their role in integrating variable sunlight and wind power. Moreover, numerous case studies highlight the effectiveness of sunlight-powered heaters in various residential settings.
One notable example is a household in Southern California that achieved a 70% reduction in energy expenses after installing a water warming system combined with a heat exchanger. Such implementations not only contributed to significant savings but also aligned with sustainability efforts. As photovoltaic panels convert sunlight into electricity, they demonstrate that is sun a renewable resource that can be utilized sustainably and indefinitely, without adverse environmental impacts.
Furthermore, the transformative impact of California’s building codes and NEM 3.0 has created new opportunities for homeowners, encouraging the adoption of renewable energy technologies. The incorporation of AI in photovoltaic efficiency also plays a crucial role, optimizing power output and system performance. As emphasized by prominent climate expert Cristen Hemingway Jaynes, ‘the 2°C climate warming target is no longer viable,’ underscoring the urgency of shifting to renewable sources such as photovoltaic power in our battle against climate change.
Furthermore, the recent Inflation Reduction Act provides key tax credits that support photovoltaic installations, although challenges in interconnection, equipment procurement, and labor availability remain headwinds. With renewable power’s potential for sustainability and its ongoing advancements, it presents a promising path forward in the global power landscape.
How Solar Power Generation Works
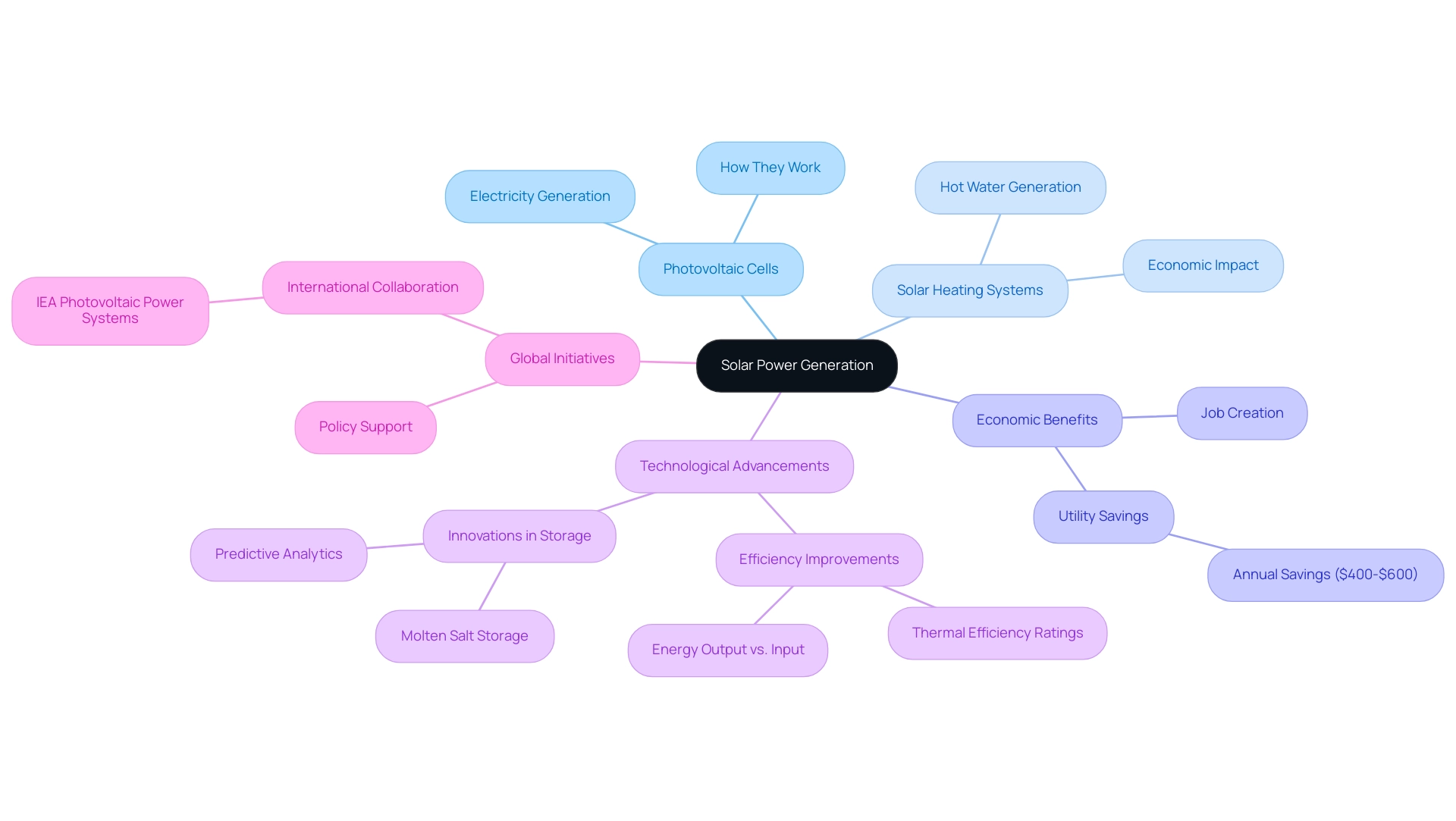
At the core of sunlight power generation are photovoltaic (PV) cells, constructed from semiconductor materials that efficiently absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity. When sunlight strikes these cells, it excites electrons within the material, generating an electric current. This current can be utilized immediately to power homes, stored in batteries for future use, or redirected back into the electrical grid.
Additionally, thermal systems utilize the sun’s heat to generate hot water for home use, highlighting another aspect of sunlight’s usefulness. The economic benefits are substantial; for instance, homeowners can save between $400 to $600 annually on utility bills by utilizing solar heating systems, as reported by the Energy Department. These systems also contribute to job creation and support equitable access initiatives, enhancing community engagement in renewable resources.
The efficiency of these innovations is continually improving, with advancements expected to significantly enhance performance rates by 2024. Key metrics such as thermal efficiency ratings and the comparison of energy output to input are crucial in evaluating overall performance and cost savings. Significantly, in 2020, around 150 MW of concentrated energy (CSP) was commissioned, showcasing an increasing dedication to renewable energy solutions.
Innovations such as molten salt storage in CSP plants enable electricity generation even after sunset, showcasing the adaptability and efficiency of sunlight-based solutions. Emerging technologies such as predictive analytics and artificial intelligence are playing an increasingly important role in optimizing the performance of heating systems. Joint endeavors, including initiatives from the IEA Photovoltaic Power Systems Technology Collaboration Program, concentrate on lowering costs and enhancing awareness of PV’s potential.
As highlighted by specialists, ‘Numerous global and bilateral collaboration initiatives are promoting technological advancement and policy support for photovoltaic systems.’ Furthermore, nations such as Israel are at the forefront of implementing heating systems using sunlight, establishing them as a necessity in new residential buildings, which highlights the increasing worldwide embrace of these innovations. This comprehension of sunlight technology not only highlights its efficiency but also emphasizes its critical role in reducing our reliance on non-renewable power sources while contributing to a healthier planet.
The Benefits of Harnessing Solar Energy
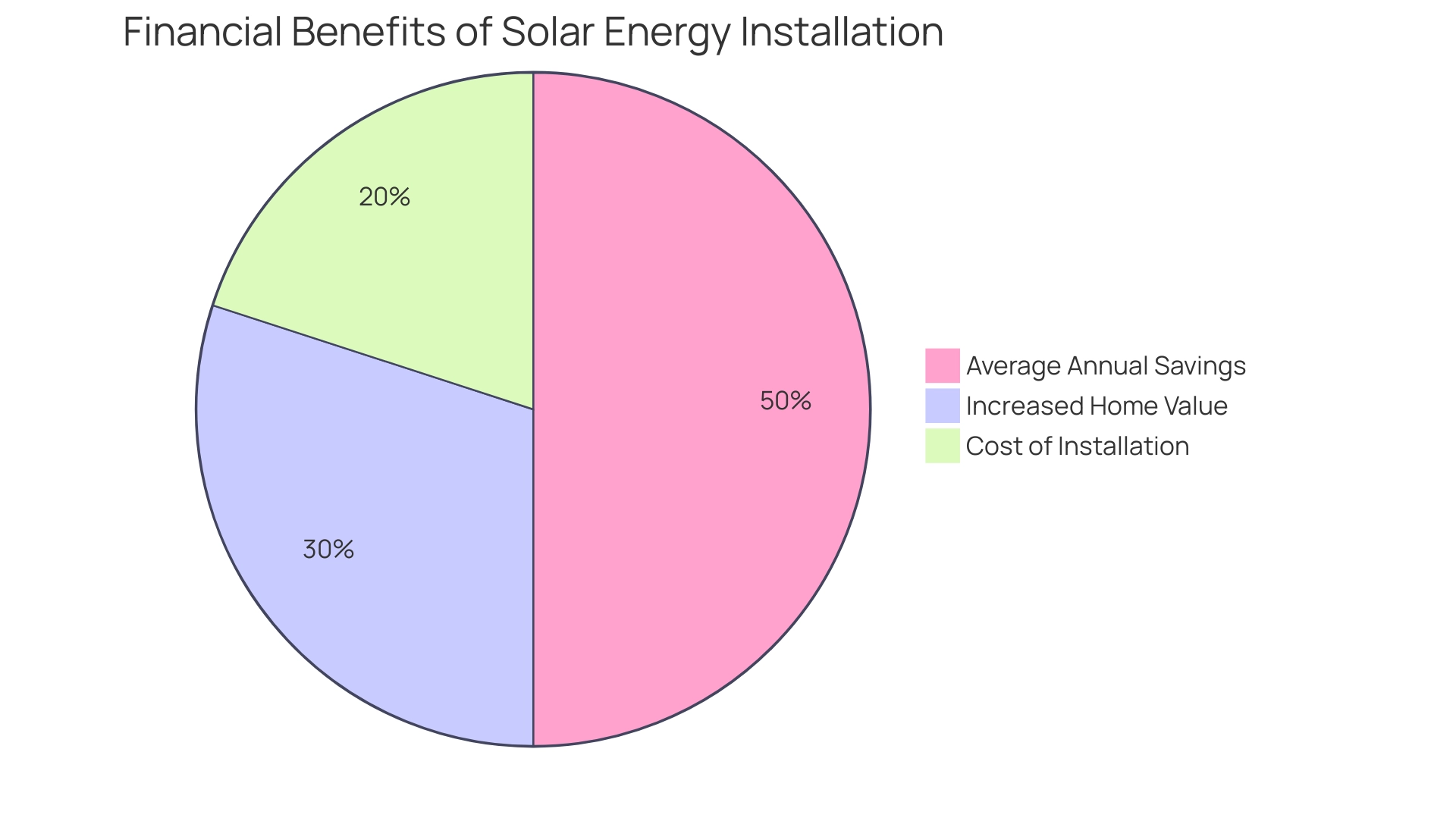
Utilizing sunlight, which raises the question of whether the sun is a renewable resource, offers numerous benefits for property owners, especially regarding cost savings and ecological effects. Renewable energy can greatly lower electricity expenses, with numerous property owners seeing decreases of 50% or greater after the setup of photovoltaic panels. In California, where families spend over $1,700 annually on electricity, the potential for savings is substantial.
Powercore Electric, being a locally-owned business with extensive understanding of California’s power requirements, guarantees that residents receive customized solutions that enhance these advantages. As Jeremy Pearl, who has been involved in the renewable energy sector since 2006 and possesses a Bachelor’s Degree in Environmental Studies from UC Santa Cruz, emphasizes, the transition to this energy source, which raises the question of whether the sun is a renewable resource, not only promotes financial benefits but also supports environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. This transition promotes independence in power, allowing homeowners to produce their own electricity, thus shielding them from the fluctuations of power prices.
With Powercore’s commitment to unmatched quality craftsmanship and a customer-first approach, your energy installation is prioritized from start to finish. It’s important to note that while the efficiency of photovoltaic panels may decline over time, the historical trend of rising electricity rates underscores the long-term financial advantage of investing in renewable energy. For example, the typical expense of a panel installation in California varies from $15,000 to $25,000, but with state and federal incentives, residents can greatly lower this initial cost.
Additionally, many satisfied customers have reported not only lower bills but also increased home value after adopting renewable energy. Moreover, the effectiveness of photovoltaic panels can differ depending on geographic region, as emphasized in the case study named ‘Location’s Role in Energy Savings,’ which demonstrates that residents in sunnier regions can attain even higher savings, particularly considering that the sun is a renewable resource. Comprehending these dynamics assists property owners in making knowledgeable choices regarding their power future while gaining advantages from Powercore Electric’s sustainable solutions.
Challenges and Limitations of Solar Energy
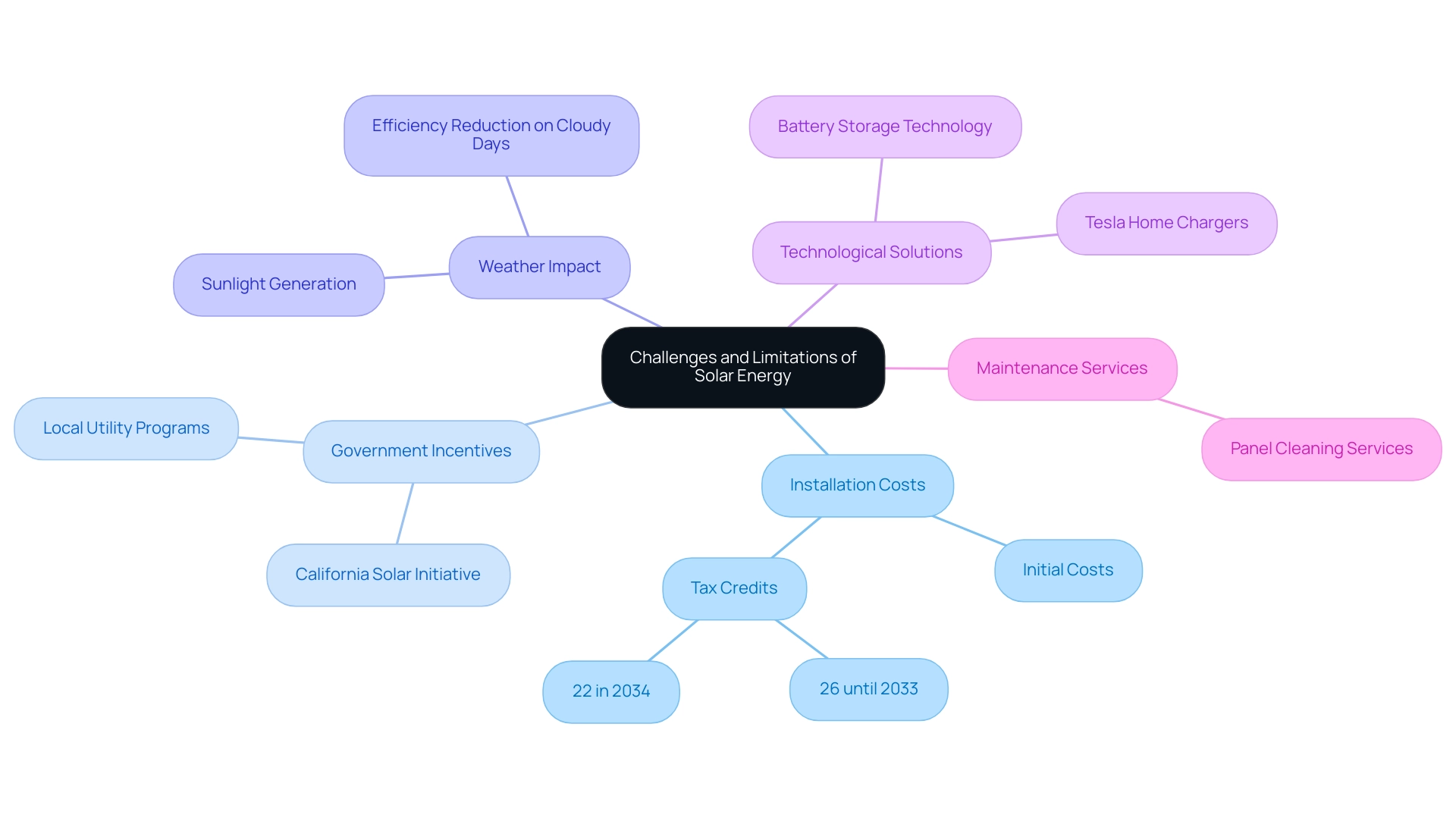
While renewable energy provides numerous benefits for eco-conscious homeowners, particularly renters in Long Beach seeking to access eco-friendly solutions, potential users must be aware of several challenges that can influence their decision-making. A primary concern is the initial installation cost, which can be considerable; however, the landscape is improving with federal tax credits currently set at 26% until the end of 2033, decreasing to 22% in 2034, alongside various local incentives such as the California Solar Initiative and programs offered by local utility companies that can ease these financial burdens. Notably, the U.S. residential renewable energy market set a record in Q3 2023 by installing 1.8 GWdc across over 210,000 projects, reflecting a 12% year-over-year increase, driven by expanding state incentives.
According to Ben Zientara, a Policy Analyst in renewable energy, ‘We have all the technology we need to do this today, but we need assistance from state and federal legislators and regulators to implement, implement, implement.’ This underscores the importance of support and financing options available to homeowners. Furthermore, it’s essential to consider that sunlight generation is influenced by weather conditions; for instance, cloudy days can significantly reduce efficiency, which raises concerns about whether the sun is a renewable resource.
The International Energy Agency forecasts that the worldwide average levelized cost of power (LCOE) for photovoltaic (PV) will be 10–15% greater in 2024 compared to 2020 levels due to inflation, supply chain challenges, and increased material expenses. Furthermore, statistics indicate that 1.1 GW of residential photovoltaic systems were installed in Q3 2024, marking a 4% decline quarter-over-quarter. Nonetheless, advancements in battery storage technology and solutions such as Tesla home chargers are assisting in tackling these issues by allowing residents to store excess power for use during times of low production.
Additionally, local panel cleaning services can help maintain efficiency by ensuring panels are free from debris and dirt. Grasping these constraints and accessible funding alternatives, along with the advantages of particular government initiatives and cleaning services, is vital for homeowners looking to make knowledgeable decisions about incorporating renewable power into their residences.
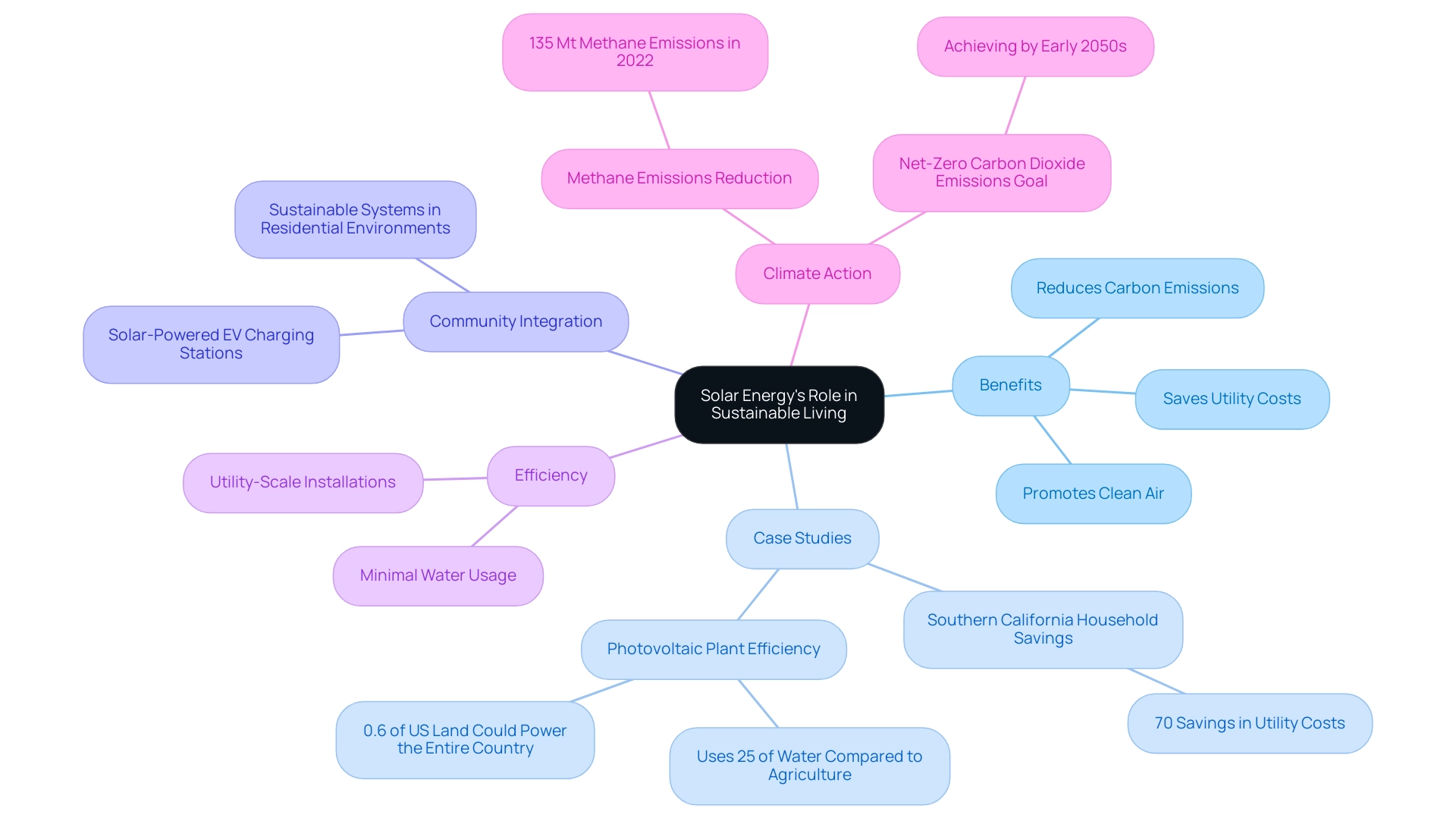
Solar Energy’s Role in Sustainable Living and Climate Action
The discussion around solar power often includes the question of whether the sun is a renewable resource, which is instrumental in advancing sustainable living and addressing climate change. By diminishing reliance on fossil fuels, photovoltaic energy significantly reduces carbon emissions, a primary driver of global warming. The implementation of renewable resources raises the important question of whether the sun is a renewable resource, as it not only encourages cleaner air and a healthier planet but also integrates smoothly into community planning, promoting local autonomy and resilience.
Numerous case studies highlight the effectiveness of sunlight heating technologies in various climates; for instance, a household in Southern California experienced over 70% savings in utility costs through an innovative water heating system combined with a heat exchanger. Furthermore, passive power collection designs have demonstrated effectiveness even in cooler areas, showcasing the relative efficiency of heating systems under various circumstances. Significantly, a photovoltaic plant requires merely 25% of the water that agriculture would need for a comparable land area, underscoring its efficiency.
Moreover, utility-scale photovoltaic installations do not release carbon dioxide or other pollutants, and merely 0.6% of the US land area could supply power for the entire nation, leading to the question of whether the sun is a renewable resource. As Matthew Eisenson from the Renewable Resources Legal Defense Initiative states, achieving net-zero carbon dioxide emissions by the early 2050s will necessitate establishing a vast number of renewable facilities in a condensed timeframe. The transformative effect of California’s building regulations and NEM 3.0 on renewable technology adoption presents significant opportunities for property owners, as they enable the integration of sustainable systems into residential environments.
As homeowners and businesses increasingly invest in renewable energy solutions, such as solar-powered EV charging stations in Los Angeles and optimized roof designs in San Diego, the cumulative effect can propel us toward achieving sustainability goals and climate action initiatives. This is especially pressing considering that methane emissions from fuel combustion and leaks reached nearly 135 Mt in 2022, further highlighting the necessity for a rapid shift to renewable power sources such as photovoltaic energy.
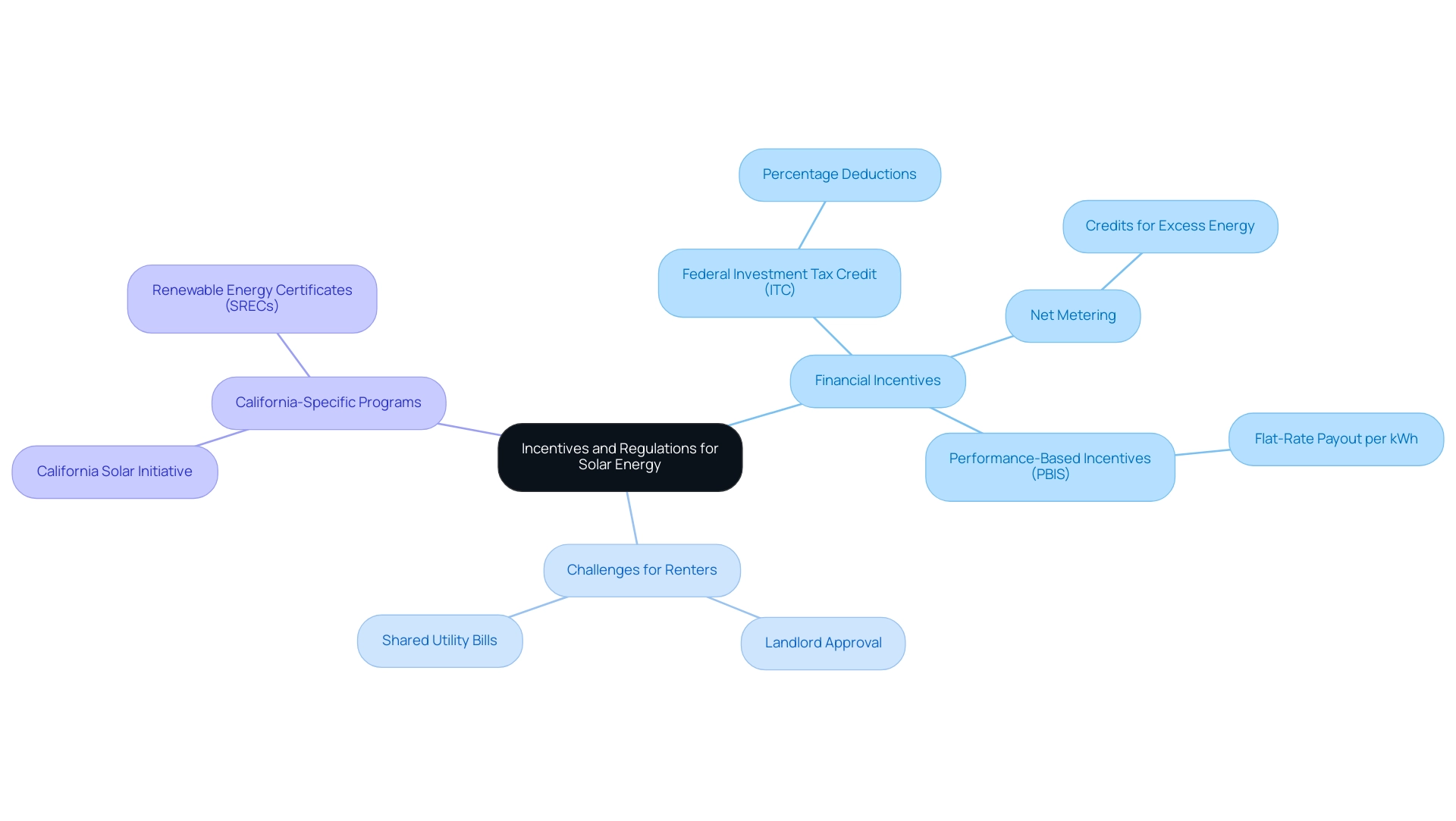
Navigating Incentives and Regulations for Solar Energy
Navigating the landscape of incentives and regulations is crucial for eco-conscious renters in Long Beach considering renewable energy adoption. California provides a range of rebates, tax credits, and financing programs aimed at promoting energy installations. A cornerstone of these incentives is the federal investment tax credit (ITC), allowing property owners to deduct a significant percentage of their installation expenses from their federal taxes, presenting a strong financial motivation.
Additionally, net metering policies enable homeowners to earn credits for excess energy produced by their systems, which is fed back into the grid. However, renters may face challenges, such as needing landlord approval for energy installations. Programs specific to California, like the California Solar Initiative, provide additional rebates that can help alleviate upfront costs for renters who can negotiate with property owners.
Furthermore, while energy systems can generate Renewable Energy Certificates (SRECs) in some markets, Long Beach renters may not have access to similar programs, which could limit potential revenue streams. Performance-Based Incentives (PBIS) also offer a flat-rate payout for every kWh of sunlight-generated power, enhancing the return on investment (ROI) for homeowners. It’s important for renters to consider the potential drawbacks of renewable power solutions, such as the initial costs and the impact of shared utility bills.
Understanding these incentives and challenges significantly alleviates the financial burden of transitioning to solar energy, especially since many eco-conscious renters in Long Beach are eager to explore if the sun is a renewable resource.
Conclusion
Solar energy stands out as a pivotal solution in the quest for sustainable living and climate action. By harnessing the sun’s inexhaustible power, homeowners can significantly reduce their electricity bills while contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The advancements in solar technology, including photovoltaic cells and solar thermal systems, have made solar energy more efficient and accessible, allowing users to generate their own power and insulate themselves from fluctuating energy prices.
However, transitioning to solar energy is not without its challenges. The initial installation costs and reliance on favorable weather conditions can pose barriers, yet various federal and state incentives, such as tax credits and net metering, help alleviate these financial burdens. As the residential solar market continues to grow, driven by supportive policies and increased awareness, more individuals are recognizing the long-term economic and environmental benefits of solar energy.
Ultimately, the adoption of solar energy is crucial in the global effort to combat climate change and foster a sustainable future. As communities increasingly embrace solar technologies, the cumulative impact can lead to cleaner air, energy independence, and a significant reduction in reliance on fossil fuels. The time to act is now; as more households invest in solar solutions, the path toward a healthier planet and a sustainable energy future becomes clearer and more attainable.