Overview
Sunlight is considered a renewable resource due to its inexhaustible nature and daily availability, allowing it to be harnessed indefinitely without depleting its supply. The article emphasizes this by detailing advancements in solar technology and the significant environmental benefits of utilizing solar energy, which collectively illustrate its potential to contribute to sustainable energy solutions and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Introduction
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, sunlight emerges as a beacon of hope, representing one of the most abundant and inexhaustible renewable resources available. As the demand for clean energy surges, homeowners in regions like Southern California are discovering the myriad benefits of harnessing solar power, from significant cost savings to reduced carbon footprints.
With technological advancements making solar solutions more accessible than ever, the shift towards renewable energy is not just a trend but a vital step towards a greener future. This article explores the transformative role of solar energy, its practical applications in everyday life, and the economic advantages that come with investing in this powerful resource, all while dispelling common misconceptions and highlighting the promising innovations on the horizon.
Understanding Renewable Resources: The Role of Sunlight
Renewable resources are natural assets that can regenerate naturally over time, and this raises the question: is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable, as it stands out as a prime example? With its daily availability and abundance, sunlight prompts the inquiry of whether it is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable, making it a cornerstone of sustainable power solutions. In contrast to fossil fuels, which are limited and lead to environmental harm, the discussion about whether is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable highlights its ability to be utilized without exhausting its supply, making it an essential resource for eco-aware homeowners in Southern California.
Recent advancements in sunlight technology, such as sun-powered EV charging stations emerging across Los Angeles and innovative roof designs optimizing light capture in San Diego, have further amplified its viability in residential settings. As global trends shift, it raises the question of whether sunlight is renewable or nonrenewable, as it is projected to play an increasingly significant role in electricity generation, contributing to the forecast that ‘Renewables are on track to become the largest source of electricity generation in the world by the end of 2027, surpassing coal and accounting for 35% of all production,’ as noted by the International Energy Agency (IEA). This transition emphasizes the significance of investing in photovoltaic solutions, especially in developing economies such as China and India, where there is an increasing dedication to understanding whether is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable.
Homeowners seeking eco-friendly alternatives can leverage this abundant resource to reduce their carbon footprint and embrace a sustainable lifestyle. With reliable partners like Powercore Electric providing complimentary tailored assessments, now is the moment to investigate the advantages of independence, financial savings, and sustainability through renewable power solutions. Reach out to Powercore Electric today to benefit from our promotional offer and obtain your complimentary personalized estimate, ensuring you maximize renewable resources for your home.
Why Sunlight is Inexhaustible: Characteristics of a Renewable Resource
Sunlight is deemed inexhaustible due to its continual availability and the fact that human consumption does not deplete it. Each day, the Earth is bombarded with approximately 5.4 Yottawatts (YW) of sunlight, a figure that significantly exceeds global power requirements. This natural replenishment raises the question of whether sunlight is renewable or nonrenewable, positioning it as a resource that can be harnessed indefinitely, offering substantial economic and environmental benefits, especially for homeowners in regions like Long Beach.
Technological improvements in photovoltaic efficiency have made it more feasible to transform this plentiful energy into usable power, thereby increasing its dependability for sustainable living. Moreover, community energy programs provide a practical solution for individuals lacking roof space for photovoltaic systems, enabling them to engage in local renewable projects and gain from shared ownership. As of April 2024, there are 37 community energy programs across 23 states, offering an alternative for those unable to install panels on their properties.
The renewable power sector is witnessing considerable expansion, with 263,883 photovoltaic workers in the U.S. as of December 2022, indicating an increase of nearly 9,000 positions (3.5%) since 2021. As Bidhan Bhuson Roy aptly puts it, ‘Solar power is an essential source in the transition to clean sources, raising the question of whether is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable, because the sun delivers more power than we’ll ever need.’ This highlights the immense potential of sunlight-based power in job creation and economic resilience, as well as its critical role in decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
By examining both active and passive heating systems, eco-conscious homeowners can make informed choices that not only contribute to their long-term savings but also support a sustainable and equitable energy future. Active heating systems utilize pumps and controls to circulate heat transfer fluids, providing consistent heating and efficient management of heat distribution, though they involve more complex installations and higher upfront costs. In contrast, passive thermal heating systems depend on building design and materials to enhance heat absorption without mechanical devices, making them simpler and less expensive to install.
Homeowners should consider their specific power requirements, architectural style, and climate adaptability when choosing between these systems to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Benefits of Harnessing Solar Energy
Utilizing sunlight, as we consider whether is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable, is vital for greatly decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and serves a key function in the battle against climate change. As the U.S. is projected to increase renewable energy capacity from 74 gigawatts in 2022 to an impressive 1,600 gigawatts by 2050, it raises the question: is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable, emphasizing the urgency for homeowners to transition from fossil fuels to this clean energy source. This shift not only allows for a reduction in carbon footprints but also contributes to cleaner air and a healthier planet.
For example, many case studies demonstrate that households employing heating technologies, such as water heaters and air heaters, have achieved significant savings; a Southern California residence reported over a 70% reduction in costs after installing a water heating system. These technologies are versatile, suitable for various residential scenarios, including:
- Heating water for domestic use
- Providing space heating
Furthermore, photovoltaic systems function with minimal water consumption compared to conventional power plants, which usually utilize large amounts of water for cooling.
This effective water usage further emphasizes the ecological advantages of renewable power, leading to the question: is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable? Moreover, Powercore Electric stands out as a leading provider in California, offering unmatched quality craftsmanship and local expertise tailored to the unique energy needs of communities. With their dedication to sustainable power solutions and a customer-first approach, residents can trust Powercore to provide tailored service that not only maximizes savings but also aligns with eco-conscious values.
As we look towards a future where over 90% of photovoltaic materials can be recycled, it becomes increasingly clear that the sustainability and long-term viability of renewable sources, including the question of is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable, are essential cornerstones of our power future.
Practical Applications of Solar Energy in Everyday Life
Solar power offers a wealth of practical applications that can transform everyday living for eco-conscious homeowners. By placing photovoltaic panels on rooftops, households can produce their own electricity, significantly reducing dependence on grid power and resulting in considerable savings on utility bills. The overall expense of residential photovoltaic systems has significantly dropped from $8.70 per watt in 2010 to merely $3.16 per watt in 2022, making this power source more attainable than ever.
This significant reduction in costs highlights the growing recognition among homeowners of the benefits associated with renewable power sources and prompts the inquiry: is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable? Moreover, solar water heaters and solar-powered devices have become popular, encouraging efficient resource use within households. These advancements not only promote independence in resources but also support a sustainable lifestyle that resonates with eco-conscious individuals.
In 2023, the primary motivation for homeowners installing batteries was access to backup power, illustrating a shift towards self-sufficiency in energy management. As policy analyst Ben Zientara notes, ‘The 2024 report is our second annual publication, utilizing data from our survey about installer-preferred brands and featuring new data about stateside manufacturing capacity.’ This statement emphasizes the growing importance of renewable technologies in contemporary households, particularly the question of whether sunlight is renewable or nonrenewable.
Furthermore, the International Energy Agency predicts that the global average levelized cost of power for photovoltaic systems will be 10–15% greater in 2024 compared to 2020 figures, owing to inflation and supply chain issues, indicating possible future cost factors for property owners. Homeowners can also benefit from various government renewable energy initiatives that explore whether sunlight is renewable or nonrenewable, which often offer financial incentives, tax credits, and grants to lower the initial investment and improve the overall return on investment. Furthermore, when assessing renewable solutions, choosing the appropriate battery is essential; property owners should analyze alternatives based on capacity, efficiency, and compatibility with current systems.
With a rise in photovoltaic panel installations throughout residential neighborhoods, property owners are not merely questioning whether sunlight is renewable or nonrenewable, but are actively adopting it as a forward-thinking measure toward a more sustainable future.
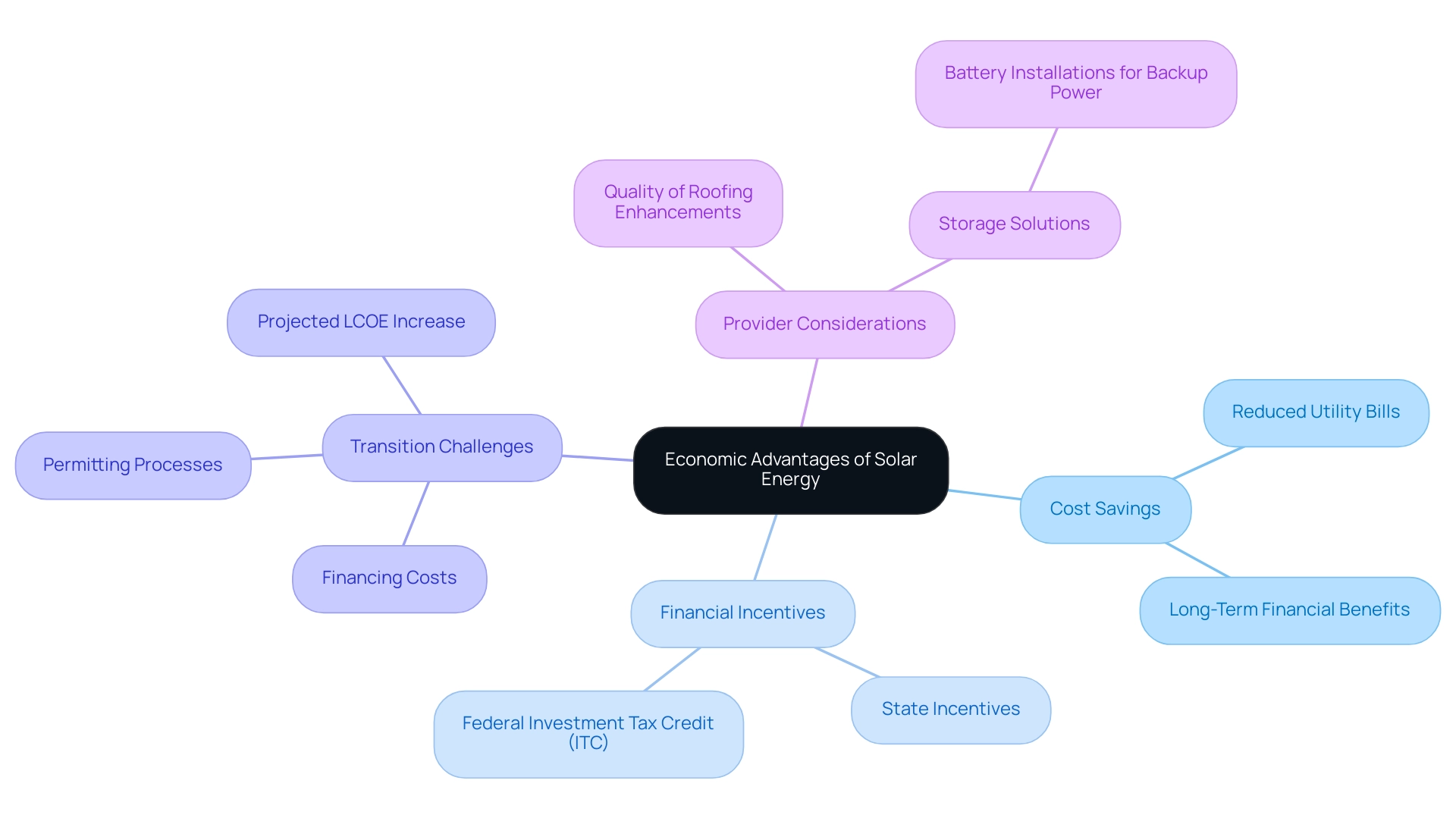
Economic Advantages of Solar Energy: Savings and Incentives
Investing in renewable energy provides eco-conscious homeowners a unique chance for substantial cost savings while enhancing their energy independence and home protection. By utilizing renewable energy, families can dramatically reduce or even eliminate their monthly utility bills, translating to considerable long-term financial benefits. Furthermore, enhancing home protection through roofing upgrades is a vital component of this investment, as a new roof can shield against weather-related damages while complementing energy installations.
The transition to renewable sources, however, can be complex, with challenges such as financing costs and permitting processes. Fortunately, many states are stepping up with various financial incentives, tax credits, and rebates to ease the initial investment. Importantly, the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) permits homeowners to deduct a significant percentage of their expenses related to photovoltaic systems from their federal taxes, making the transition to renewable sources even more attractive.
As the economic landscape changes, projections suggest that the global average levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for photovoltaic systems will increase by 10–15% in 2024 compared to 2020 due to inflation and supply chain challenges. Despite these challenges, the financial benefits of sunlight power raise the important question of whether is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable. Industry leaders like Amazon, Google, and Meta exemplify the potential for resource savings with a combined contracted pipeline of over 25 GW.
Additionally, with 85% of installers using NREL’s SolarAPP+ permitting software indicating that it streamlines the permitting process, embracing renewable energy solutions is becoming increasingly attainable for property owners. While many initially seek savings through photovoltaic panels, there is a notable shift towards prioritizing power security, particularly with the growing interest in battery storage for backup power. This trend highlights the significance of resilience in power solutions, as property owners increasingly opt for battery installations mainly for backup electricity rather than just for financial benefits.
When assessing service providers, homeowners should take into account not just the financial factors but also the quality of roofing enhancements and storage solutions available to ensure they discover the best value for their investment.
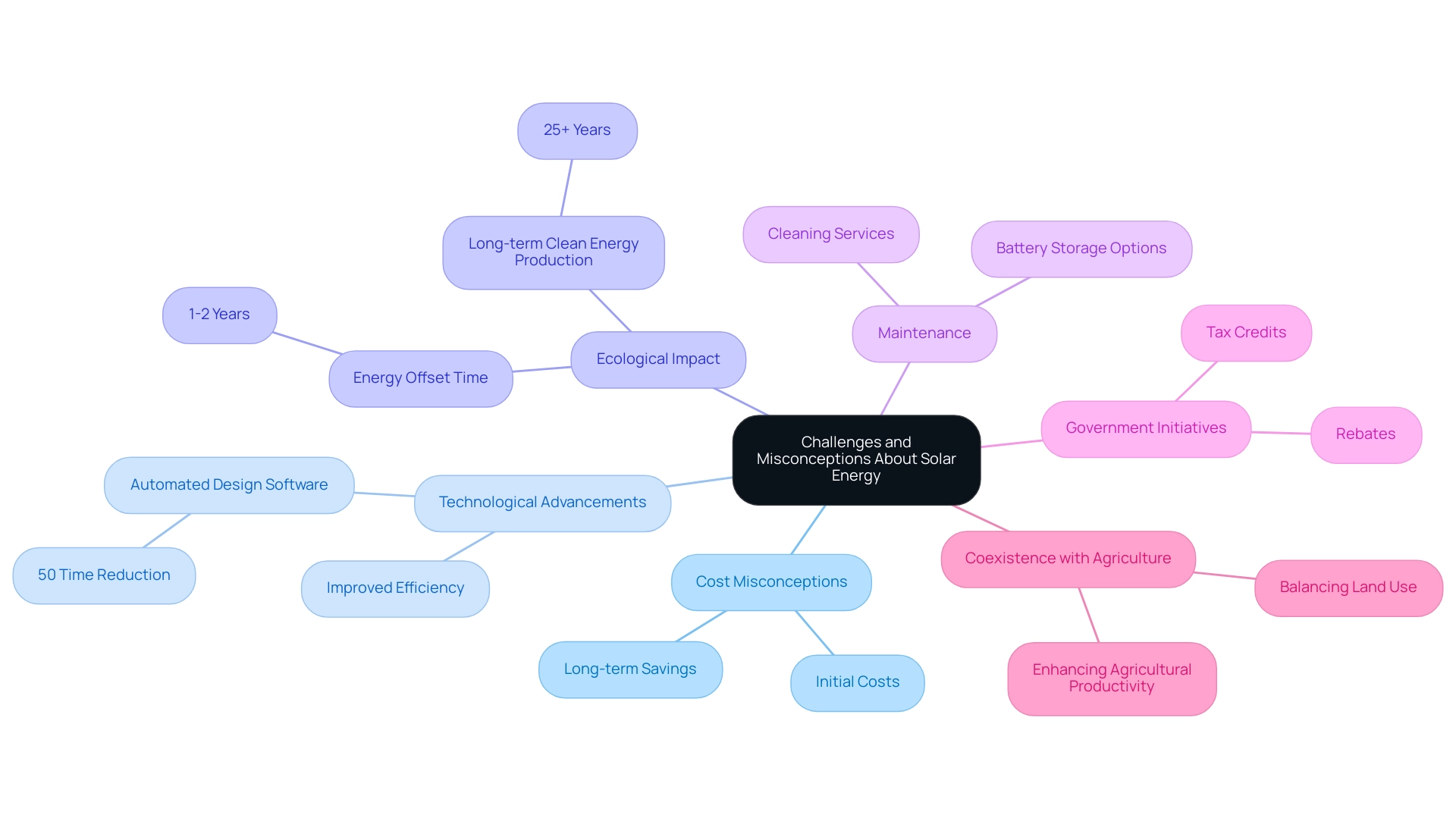
Challenges and Misconceptions About Solar Energy
Solar energy, despite its numerous advantages, is often clouded by misconceptions. Numerous people erroneously think that photovoltaic systems are excessively costly or inefficient in less bright conditions. However, technological advancements have significantly increased the affordability and efficiency of photovoltaic systems, making them a viable option even in cloudy climates.
For instance, automated design software can cut layout time by up to 50%, streamlining installation processes and reducing costs. The ecological effect of creating photovoltaic modules is surpassed by the advantages of generating clean energy; a photovoltaic device compensates for its production energy in only 1-2 years and continues to generate clean energy for more than 25 years. Alongside conventional energy systems, Long Beach renters can investigate creative alternatives such as Tesla home chargers and roofing shingles that offer both visual appeal and practicality.
Cleaning services are also available to maintain panel efficiency, ensuring optimal performance over time. Battery choices for homeowners enable power storage, optimizing the use of generated renewable power. Government initiatives provide incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, making renewable power more accessible.
While the initial investment might seem daunting, the long-term savings on utility bills and available incentives frequently surpass the upfront expenses. Moreover, case studies, like the balance between agricultural productivity and photovoltaic development, demonstrate how this form of power can coexist with other land uses, enhancing its practicality. For instance, particular metrics indicate that farms incorporating photovoltaic systems can enhance their overall productivity while producing renewable power.
By tackling these misunderstandings and offering perspectives on government initiatives and accessible technologies, we can encourage wider acceptance and comprehension of photovoltaic power as a practical and sustainable renewable resource, especially in answering the question of whether is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable for eco-conscious homeowners.
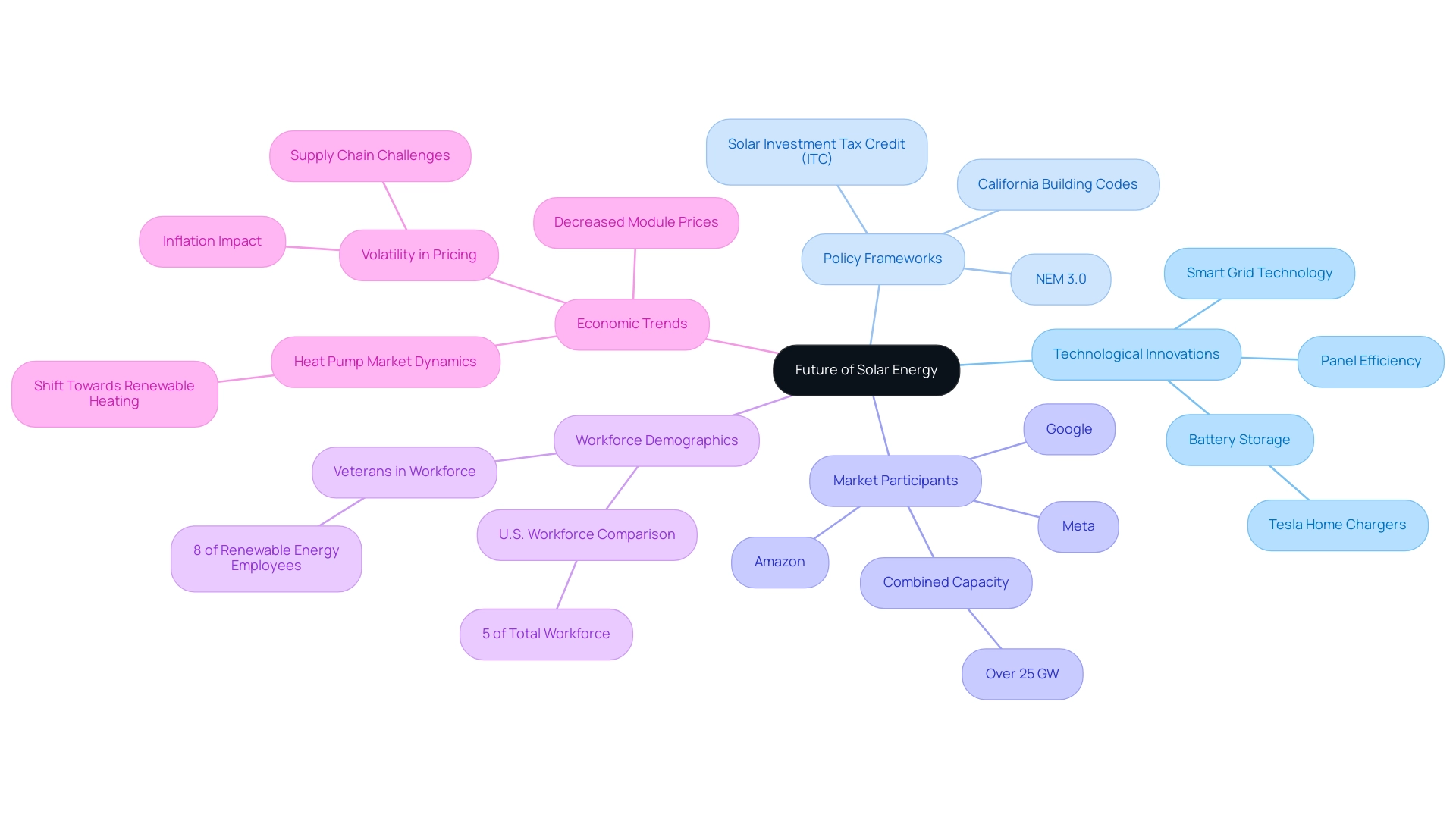
The Future of Solar Energy: Innovations and Policy Directions
The outlook for renewable power is increasingly optimistic, driven by a surge of technological advancements and supportive policy frameworks such as California’s transformative building codes and NEM 3.0. Innovations in panel efficiency, enhanced battery storage systems, including options like Tesla home chargers, and the integration of smart grid technology are all poised to significantly improve the effectiveness of renewable installations. Key participants in the sector, such as Amazon, Google, and Meta, have created a collective contracted pipeline exceeding 25 GW of capacity, as noted in SEIA’s annual Solar Means Business report, demonstrating a strong dedication to renewable solutions.
Furthermore, the diverse nature of the energy sector is evident, with 8% of all renewable energy employees being veterans, compared to 5% of the U.S. workforce. Government initiatives, such as the Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and various state-level incentives, encouraging the adoption of renewable energy have become increasingly pronounced, creating a supportive landscape for growth. However, it’s important to note that pricing for renewable energy has experienced volatility over the past three years due to inflation and supply chain challenges.
Yet, recent easing of disruptions has led to a decrease in module prices, making renewable energy solutions more accessible. As evidenced by the heat pump market dynamics, where heat pumps are steadily gaining market share over fossil fuel boilers in Europe, the shift towards renewable heating solutions is underway. This trend highlights the growing recognition among homeowners of solar energy’s economic and environmental benefits, which raises the question of whether is sunlight renewable or nonrenewable and sets the stage for solar energy to become a cornerstone in the global transition to sustainable energy practices.
Conclusion
Harnessing solar energy represents a pivotal shift towards sustainability, offering both environmental and economic benefits that are increasingly hard to ignore. Sunlight, as an inexhaustible resource, provides homeowners with a reliable source of energy that can significantly reduce carbon footprints while promoting energy independence. With advancements in solar technology and the decreasing costs of solar installations, homeowners in regions like Southern California can now access renewable energy solutions that were once deemed unattainable.
The practical applications of solar energy are vast, from reducing monthly utility bills to powering everyday appliances, making it an attractive option for eco-conscious individuals. Moreover, the economic advantages, including various financial incentives and tax credits, make transitioning to solar power not only feasible but also financially rewarding. As the solar energy sector continues to grow, it also promises to create jobs and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Addressing misconceptions about solar energy is crucial for fostering broader acceptance. By highlighting the technologies and government programs available, potential adopters can make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals. As the future of solar energy looks promising, with ongoing innovations and supportive policies, it is clear that embracing solar power is not just a personal choice but a collective step towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future. The time to act is now, as the benefits of solar energy extend far beyond individual households, contributing to a healthier planet for generations to come.