Overview
Solar powered heaters for homes provide significant benefits, including reduced energy costs and a lower environmental impact by harnessing renewable energy from the sun. The article highlights that these systems can lead to savings of 50% to 80% on heating expenses, and their adoption contributes to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions, making them an attractive choice for eco-conscious homeowners.
Introduction
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability and renewable energy, solar-powered heaters stand out as a practical solution for eco-conscious homeowners. By harnessing the sun’s energy, these systems provide an efficient means of heating water for various domestic purposes, from bathing to maintaining swimming pools. As technology advances in 2024, the appeal of solar water heating systems grows, promising not only environmental benefits but also significant financial savings.
With a myriad of options available, understanding the differences between active and passive systems, evaluating cost implications, and exploring available financial incentives can empower homeowners to make informed decisions. This article delves into the fundamentals of solar-powered heaters, offering a comprehensive guide to their functionality, installation, and maintenance, while highlighting their role in promoting a sustainable future.
Introduction to Solar-Powered Heaters: Basics and Functionality
A solar powered heater for home captures the sun’s energy to efficiently warm liquid for various household purposes, including bathing, cooking, and keeping swimming pools. These setups function by using collectors that capture sunlight and transform it into heat, transferring this thermal energy to fluid stored in a tank, thus creating a renewable and sustainable energy source. In 2024, advancements in technology have further improved the efficiency of solutions like a solar powered heater for home, making them an attractive option for eco-conscious homeowners.
For example, when examining two heating system models, the extra expense of a more efficient model is only $85, with a payback period of 1.5 years, highlighting the financial advantages of investing in these systems. Homeowners should also consider key factors such as:
- Regional climate
- Household size
- Hot usage requirements
to determine the right capacity for their solar heater. The First Hour Rating (FHR) is another important metric to evaluate, as it measures the amount of hot water a heater can supply in the first hour of use.
Furthermore, ease of installation and maintenance are vital factors to consider, as setups that come with comprehensive warranties and trustworthy manufacturer support ensure long-term satisfaction and peace of mind. Moreover, Jordan’s Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources has introduced an online platform assisting inquiries regarding its subsidy program for residential heating systems, providing financial incentives that encourage the use of renewable resources. As Kalyani Raje, Senior Research Analyst at Cognitive Market Research, notes, the thermosiphon segment had the largest share in the global Solar Water Heater market due to its reliability and simplicity.
As property owners grow more conscious of the long-term savings and environmental advantages offered by a solar powered heater for home in contrast to conventional heating approaches, the attraction of such options keeps growing. Furthermore, the growing pipeline for large-scale solar heat plants signals a broader trend within the industry, reinforcing the significance of solar heating solutions in the transition toward sustainable energy.
Types of Solar Water Heating Systems: Active vs. Passive
Solar water heating solutions can be broadly categorized into two types: active and passive. Active setups, which incorporate circulating pumps and control mechanisms, utilize both exterior and interior space, making them particularly beneficial for homeowners in colder climates who seek higher efficiency and functionality. These setups encompass:
- Direct circulation models, created for regions that do not experience freezing temperatures.
- Indirect circulation models, which utilize a non-freezing heat-transfer fluid appropriate for colder areas.
For instance, recent innovations indicate that active technologies can significantly lower utility bills, even in older homes with less effective insulation. As emphasized by Professor Saleem Raza Samo, ‘The renewable resource that is plentiful in Pakistan is sunlight, demonstrating an annual irradiance of approximately 1900-2200 kWh/m²,’ highlighting the capability in sun-drenched areas. Moreover, under intense solar radiation of over 800 W/m², the efficiency of these setups can be greatly enhanced.
Conversely, passive solar solutions operate without pumps, relying on natural convection, which simplifies installation and often reduces costs. These setups primarily occupy exterior space and are generally more appropriate for warmer climates, featuring models such as:
- Batch setups
- Integral collector-storage configurations
Understanding the advantages and limitations of both setups is crucial for eco-conscious homeowners to make informed decisions regarding a solar powered heater for home that meets their specific heating needs and regional climate conditions.
It is essential to consider installation and maintenance costs, which can vary significantly across different models. For example, while passive setups may offer lower initial costs, active configurations often provide substantial long-term savings through enhanced efficiency and performance. Additionally, regular maintenance is vital to ensure these networks operate at peak efficiency and longevity.
Homeowners should also consider the best battery options for effective power storage, as incorporating an appropriate battery setup can improve the overall performance of a solar powered heater for home. Numerous case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of these solutions, particularly in regions like Southern California where households have reported over 70% savings on energy expenses, showcasing the sustainability and economic benefits of a solar powered heater for home.
Cost Analysis and Financial Incentives for Solar Heaters
The cost of installing a solar powered heater for home can vary significantly, typically falling between $3,000 and $5,000 depending on the type of system and the complexity of the installation. For a comparative perspective, the average cost of heaters from various brands varies: Rheem® ranges from $600 to $2,300, A.O. Smith® from $800 to $3,500, and Bradford White® from $400 to $3,000.
Despite this initial investment, eco-conscious homeowners can anticipate substantial savings on their utility bills by installing a solar powered heater for home, often recovering their costs within a span of 5 to 7 years. Significantly, thermal heating systems can save users between 50% and 80% on their heating expenses over time, making them a financially appealing choice. Furthermore, a variety of financial incentives, including federal tax credits, state rebates, and local incentives, can help offset installation costs and encourage renewable energy adoption.
As expert reviewer Jeff Botelho notes, ‘The average water heater lasts about ten years, though certain high-efficiency models can last more than 20,’ which emphasizes the long-term benefits of investing in a solar powered heater for home. Thus, it is essential for prospective buyers to conduct thorough research into available incentives and consult with an energy specialist. This will offer a clearer view of the overall financial implications of investing in heating solutions, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and sustainability objectives.
Additionally, the case study titled ‘Performance of Solar Water Heaters in Various Conditions’ illustrates that most setups require a backup heater for cold or cloudy days. However, they can retain sufficient hot water produced on sunny days for later use, further highlighting the practicality and efficiency of a solar powered heater for home systems in a comprehensive renewable power strategy. To further assist homeowners, here are the top 5 solar powered heaters for home to consider:
- [Heater Model 1]
- [Heater Model 2]
- [Heater Model 3]
- [Heater Model 4]
- [Heater Model 5]
Furthermore, Tesla charger expenses usually vary from $500 to $1,200, based on the installation details and extra features, making them a vital component of the overall energy solution for homeowners.
Installing Solar-Powered Heaters: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Site Assessment: Begin by thoroughly evaluating the location for optimal solar access. Check for shading from trees or buildings, as effective sunlight exposure is crucial for efficiency. A well-placed setup of a solar powered heater for home can significantly enhance performance, contributing to a reduction in heating utility needs by up to 83.4%. This highlights the significance of thorough site selection in maximizing the advantages of a solar powered heater for home.
- Select System Type: Determine whether an active or passive solar water heating arrangement best suits your needs and budget. Active setups, which include pumps and controls, offer more flexibility but may incur higher installation and maintenance costs. Comprehending the differences between these frameworks is essential for understanding the benefits of a solar powered heater for home. For instance, residences in cooler regions might benefit from the reliability of a solar powered heater for home, while homes in milder climates can utilize passive methods to maintain comfortable temperatures with minimal mechanical intervention.
- Purchase Equipment: Acquire essential components tailored to your chosen type. This includes collectors, storage tanks, and, if choosing an active system, pumps. Engaging with manufacturers can yield insights into the best solar powered heater for home, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Additionally, consider the best battery options for energy storage, as this is crucial for maximizing the efficiency of your energy system.
- Install Solar Collectors: Properly mount solar collectors on the roof or ground, angled to maximize sun exposure. This positioning can help achieve an impressive efficiency rate, with thermosiphon setups demonstrating around 40% efficiency even during winter months. Applying best practices, as emphasized in case studies, can further improve performance.
- Connect Plumbing: Link the collectors to the storage tank, ensuring all plumbing is properly insulated and sealed. This step is critical to prevent heat loss and ensure efficient operation of a solar powered heater for home, aligning with best practices for solar power systems.
- Install Controls: For active setups, install the necessary pumps and control mechanisms to regulate water flow. Proper control installation is essential to optimize energy use and enhance performance.
- Testing: After installation, conduct comprehensive tests to ensure the setup operates efficiently. Address any issues identified during testing to guarantee optimal performance before regular use. Regular maintenance is crucial for longevity and efficiency, ensuring that your investment continues to deliver value. Implement routine checks and cleaning practices to maintain performance and consider documenting any maintenance activities to track efficiency over time.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity and Efficiency of Solar Heaters
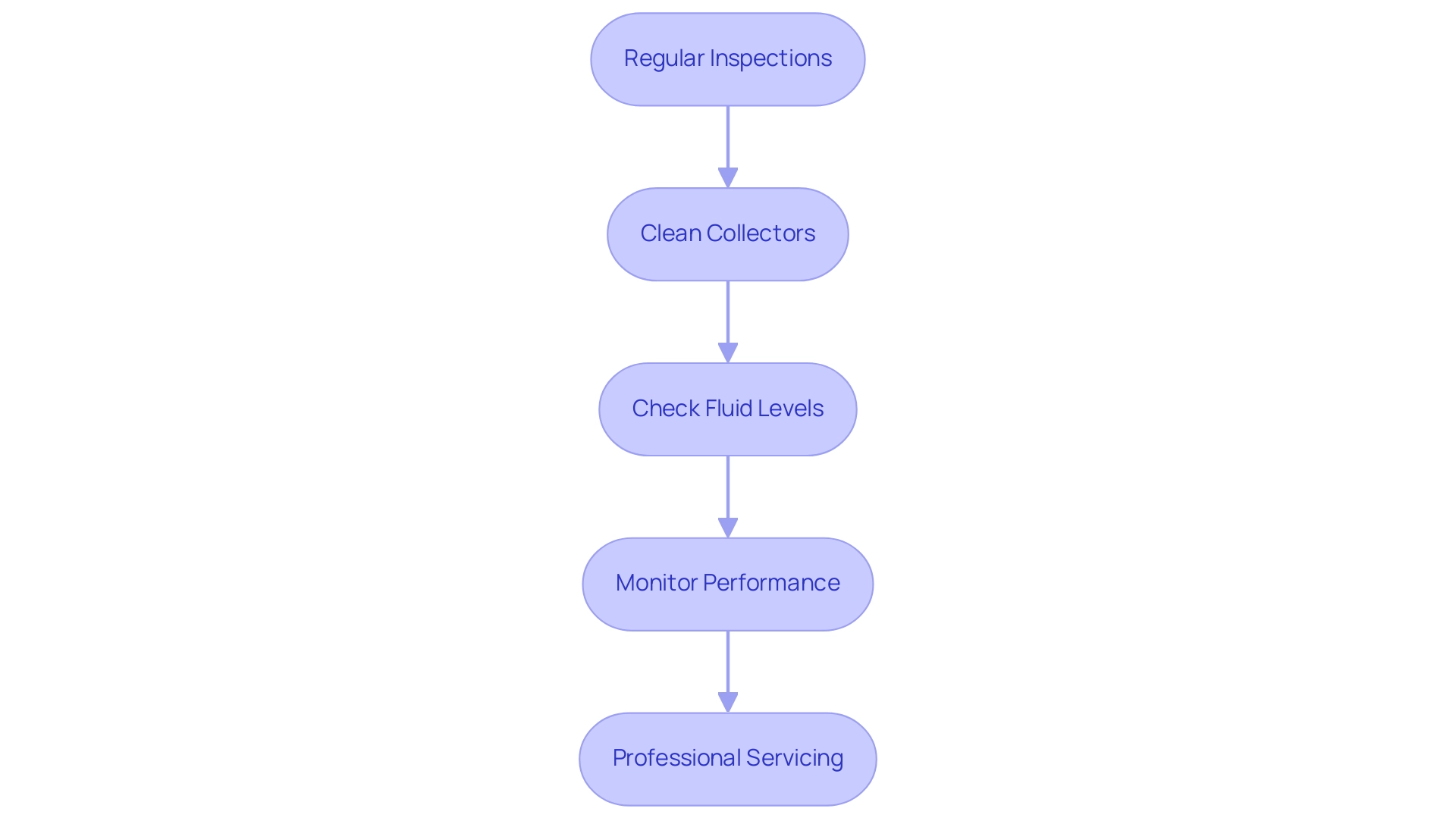
To ensure the longevity and efficiency of your solar powered heater for home, regular maintenance is essential. Here are key practices to follow:
-
Regular Inspections: Conduct routine checks for visible damage to photovoltaic collectors and the plumbing system.
Look for any leaks or signs of corrosion that could compromise performance. Remember, replacing a severely damaged water heater can often be more cost-effective than continual repairs. As one expert noted, ‘Did you notice a significant drop in power production?’
This issue can be due to a variety of factors, with the most common being dust and debris buildup.
-
Clean Collectors: Maintaining clean collectors is crucial for maximizing energy efficiency and ensuring optimal energy production. Dust, dirt, and debris can significantly reduce their effectiveness, leading to performance declines that can build up over time.
Aim to clean them every few months using a mild soap and water solution. Interestingly, researchers have created a model to estimate dust accumulation on photovoltaic panels, which can assist in determining the optimal cleaning schedule based on environmental factors.
-
Check Fluid Levels: In operational setups, it’s important to monitor the levels of heat transfer fluids.
Ensure they are at appropriate levels and replace them as necessary to maintain optimal functionality. This will also assist in improving the overall efficiency of your heating system.
-
Monitor Performance: Keep a close eye on your setup’s performance and energy output.
Identifying any significant drops in efficiency early can help prevent costly repairs down the line. With proper upkeep, sunlight heating installations can save users 50%–80% on their heating expenses over time, contributing to both economic and environmental advantages.
-
Professional Servicing: Consider scheduling annual maintenance checks with a qualified technician.
The U.S. Department of Energy observes that the monthly expense of incorporating a heating system into a new construction mortgage can be as low as $10 to $15 after tax deductions. Regular professional servicing ensures that any potential issues are addressed promptly, helping to safeguard your investment.
Additionally, while solar thermal systems may not be ideal for residential use, a solar powered heater for home can be a more efficient option, providing significant ROI in high-demand commercial applications, such as laundromats and restaurants, as highlighted in case studies.
By adhering to these maintenance tips and considering environmental factors that may require more frequent checks, you can significantly improve the efficiency and longevity of your solar powered heater for home.
This ultimately results in greater savings on your annual heating expenses, which average $457.54 for electric heaters, while also supporting your goal of a more sustainable and environmentally friendly home.
Environmental Impact: How Solar Heaters Contribute to Sustainability
A solar powered heater for home offers an appealing solution to the urgent problem of greenhouse gas emissions by utilizing renewable power sources. Numerous case studies demonstrate their effectiveness, particularly in diverse climates. For example, a household in Southern California realized over 70% savings on energy expenses with a combined heating mechanism and heat exchanger, while a home in the Pacific Northwest demonstrated the effectiveness of passive energy designs featuring large south-facing windows, significantly lowering energy costs.
These systems, such as a solar powered heater for home, effectively replace conventional fossil fuel-based heating methods, resulting in a notable reduction in air pollution and a positive contribution toward combating climate change. Statistics indicate that the overall ecological advantage of utilizing a heating system powered by the sun, per square meter, throughout its lifespan totals an impressive 750.2 CNY, with an annual average fraction of 71%—potentially achieving 100% during summer months. Furthermore, sunlight-powered air heaters can reduce a household’s carbon output by 20 to 40 percent and decrease monthly utility costs by 30 percent, according to Clean Energy Resource Teams.
Despite these benefits, hot water technology has seen low uptake in Australia, highlighting a gap between potential and actual implementation in the market. By reducing dependence on utility providers, heating systems not only decrease total power usage but also ease the pressure on our natural resources. This technology can especially benefit lower-income groups by enhancing access to power services and improving living quality, ultimately reducing the financial burden associated with power needs.
By embracing solar technology, homeowners can save on energy costs and utilize a solar powered heater for home, making a significant commitment to environmental sustainability and contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
Harnessing solar energy through solar-powered heaters not only addresses the growing need for sustainable energy solutions but also delivers significant financial and environmental benefits. These systems efficiently heat water for various domestic uses, and advancements in technology have made them more accessible and effective than ever. Understanding the differences between active and passive systems is crucial for homeowners, as each offers unique advantages tailored to specific climates and needs.
The cost analysis reveals that while the initial investment for solar heaters can be substantial, the long-term savings on energy bills make them an economically attractive choice. With the right financial incentives available, homeowners can further offset installation costs, making the transition to solar heating even more appealing. The installation process, though detailed, is straightforward, and proper maintenance ensures these systems continue to operate efficiently over time.
Ultimately, solar-powered heaters represent a vital step toward a more sustainable future. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, these systems contribute significantly to environmental preservation. Homeowners not only save money but also play a role in combating climate change and promoting energy independence. Embracing solar technology is not just an investment in home comfort; it is a commitment to a healthier planet for generations to come.