Overview
The article focuses on understanding solar panel sizes and wattage, emphasizing their importance in meeting homeowners’ energy needs and optimizing installation. It highlights that selecting the right solar panel dimensions and wattage is crucial for maximizing power output and efficiency, as evidenced by discussions on the various panel types, their dimensions, and how they align with energy consumption and roof configurations.
Introduction
As homeowners increasingly seek sustainable energy solutions, understanding the various aspects of solar panels becomes essential. From the standard sizes and dimensions that fit different roofing configurations to the wattage that determines energy output, each detail plays a crucial role in optimizing solar energy systems. With options ranging from monocrystalline to polycrystalline and thin-film panels, making the right choice can significantly impact both energy savings and environmental contributions.
This guide delves into the key factors that influence solar panel performance, helping homeowners navigate the complexities of installation, efficiency, and cost, ensuring they can harness the full potential of solar energy for their homes.
Exploring Standard Solar Panel Sizes and Dimensions
When it comes to solar systems, homeowners will find a variety of solar panel sizes and wattage that cater to different needs and roofing configurations. Typically, these units range from 60 to 72 cells. For example, a standard 60-cell module measures about 65 inches by 39 inches, while a larger 72-cell unit is approximately 77 inches by 39 inches.
These dimensions are thoughtfully designed to maximize space efficiency while delivering optimal power output. Comprehending these measurements is essential for assessing how many units can comfortably fit in your installation space, which impacts both your cost savings and the visual attractiveness of your roof.
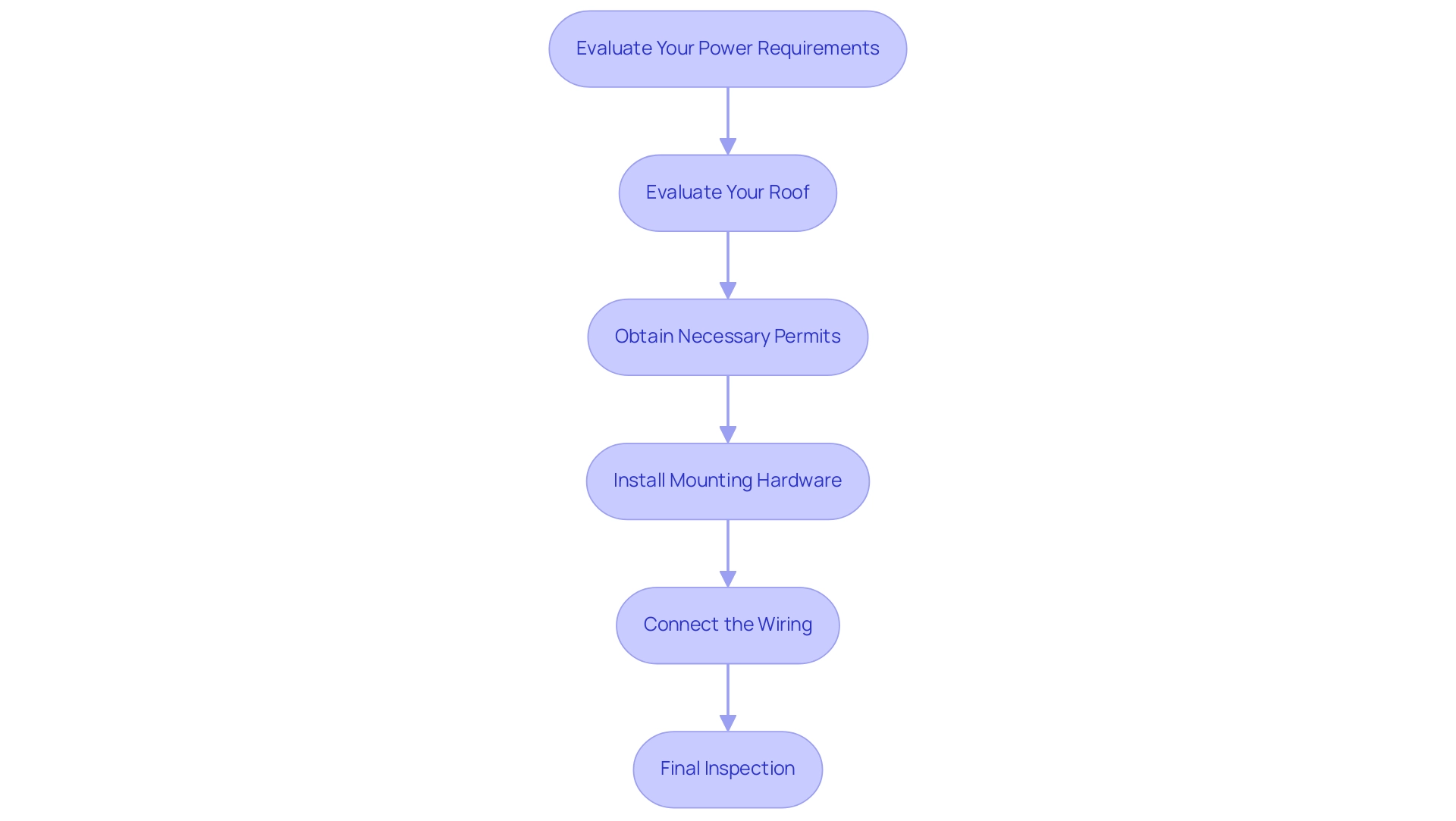
- Evaluate Your Power Requirements: Ascertain how much power you consume and how many modules you will require.
- Evaluate Your Roof: Check the condition and orientation of your roof to ensure it can support photovoltaic panels.
- Obtain Necessary Permits: Research local regulations and obtain any required permits for installation.
- Select Your Sections: Choose the appropriate size and type of sections based on your energy needs and roof space.
- Install Mounting Hardware: Securely attach the mounting brackets to your roof.
- Install the Modules: Carefully position the photovoltaic modules onto the mounting hardware.
- Connect the Wiring: Connect the units to the inverter and any necessary electrical components.
- Final Inspection: Have an expert evaluate the installation to verify everything meets regulations.
Installing photovoltaic (PV) systems can range from $5,400 to $18,000, so it’s crucial for property owners to consider the financial consequences of their choices regarding renewable energy. As Dr. Mark Z. Jacobson, Director of the Atmosphere/Energy Program at Stanford University, points out, ‘Solar PV technologies continue to improve, resulting in the continued decline in PV prices.’ This enhancement not only affects pricing but also the variety of solar panel sizes and wattage that are offered.
Furthermore, with over 2,500 utility-scale photovoltaic (PV) electricity-generating facilities in the United States, the demand for this renewable source is increasing, underscoring the importance of solar panel sizes and wattage for residential applications. In contrast, traditional electricity sources often incur higher long-term costs and contribute to environmental degradation. By transitioning to renewable energy, homeowners can lower their utility expenses and carbon footprint, creating an eco-friendly option for the future.
As renewable technologies continue to advance, homeowners will find it increasingly easier to select the appropriate solar panel sizes and wattage to meet their energy requirements, enabling them to make informed decisions for a sustainable future.
Understanding Solar Panel Wattage and Its Impact on Energy Output
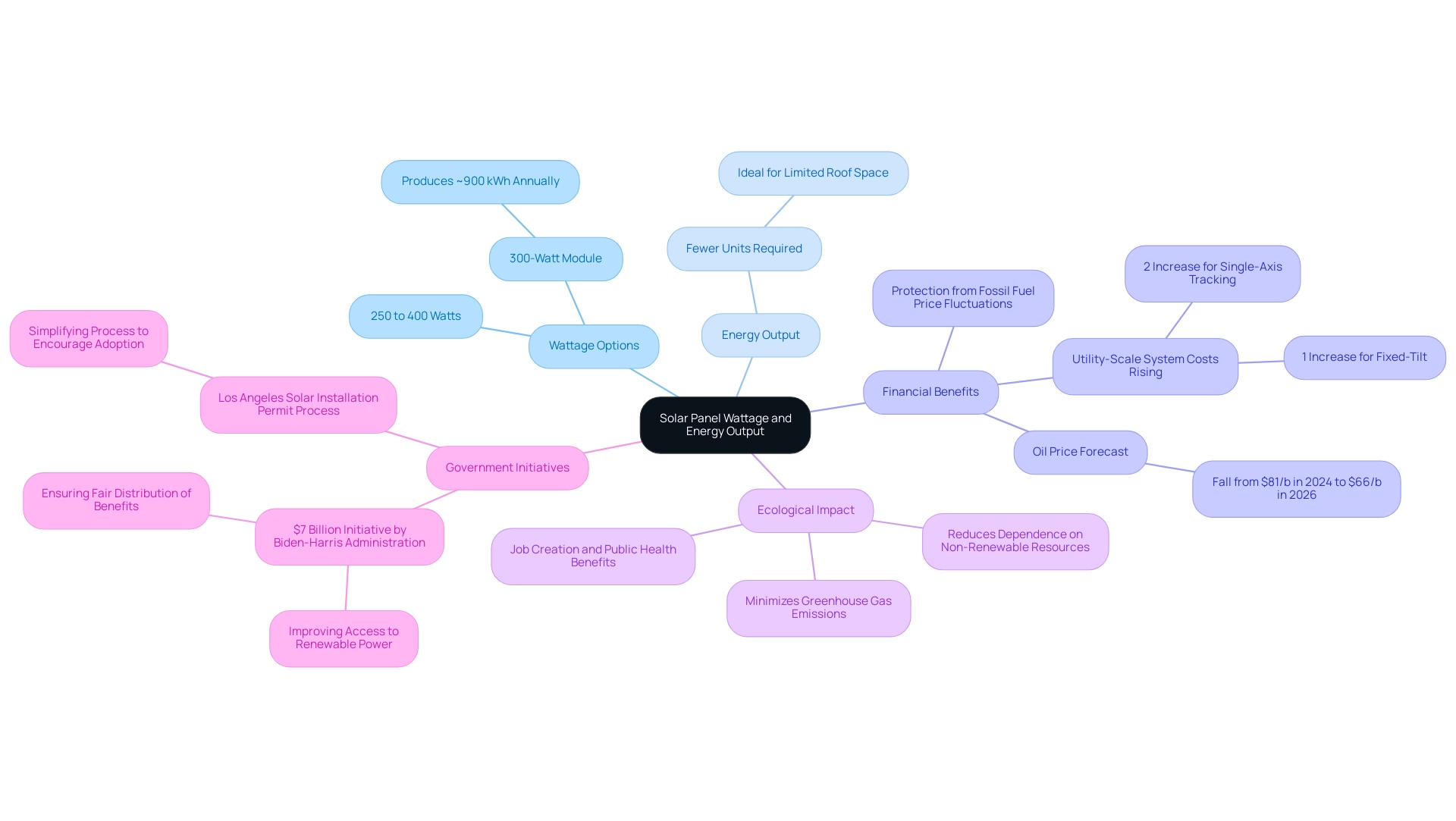
When considering solar panel sizes and wattage, you’ll typically find options ranging from 250 to 400 watts. Opting for higher wattage units can be a game-changer, especially for those with limited roof space. For instance, a 300-watt module can produce approximately 900 kilowatt-hours of electricity annually under optimal conditions, indicating that fewer units are required to satisfy your power requirements—an important benefit for smaller rooftops.
As you investigate your alternative options, consider your household’s overall power usage to determine how many panels you’ll require for efficient electricity. Investing in renewable sources is not only financially prudent, especially as utility-scale system costs rise, but it also protects you from the fluctuations of fossil fuel prices. With the U.S. Energy Information Administration predicting a drop in oil prices from an average of $81 per barrel in 2024 to $66 per barrel in 2026, shifting to photovoltaic power becomes more attractive.
Furthermore, the ecological advantages are substantial; renewable power minimizes greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on non-renewable resources, aiding in a more sustainable future. Furthermore, renewable power initiatives can result in job creation and enhanced public health outcomes, reinforcing the positive effect on communities. In Los Angeles, efforts to simplify the installation permit process for renewable energy are underway to encourage more homeowners, including renters in Long Beach, to adopt alternative solutions.
Significantly, the Biden-Harris administration’s $7 billion initiative for all aims to improve access to renewable power, ensuring fair distribution of benefits from solar resources. Understanding the solar panel sizes and wattage and their influence on power output is essential for making informed choices regarding your renewable investment and engaging in the clean power initiative!
Key Factors Affecting Solar Panel Performance and Efficiency
When considering the performance of photovoltaic systems, various essential elements can significantly impact your home’s power efficiency. Let’s break them down in a way that’s easy to understand:
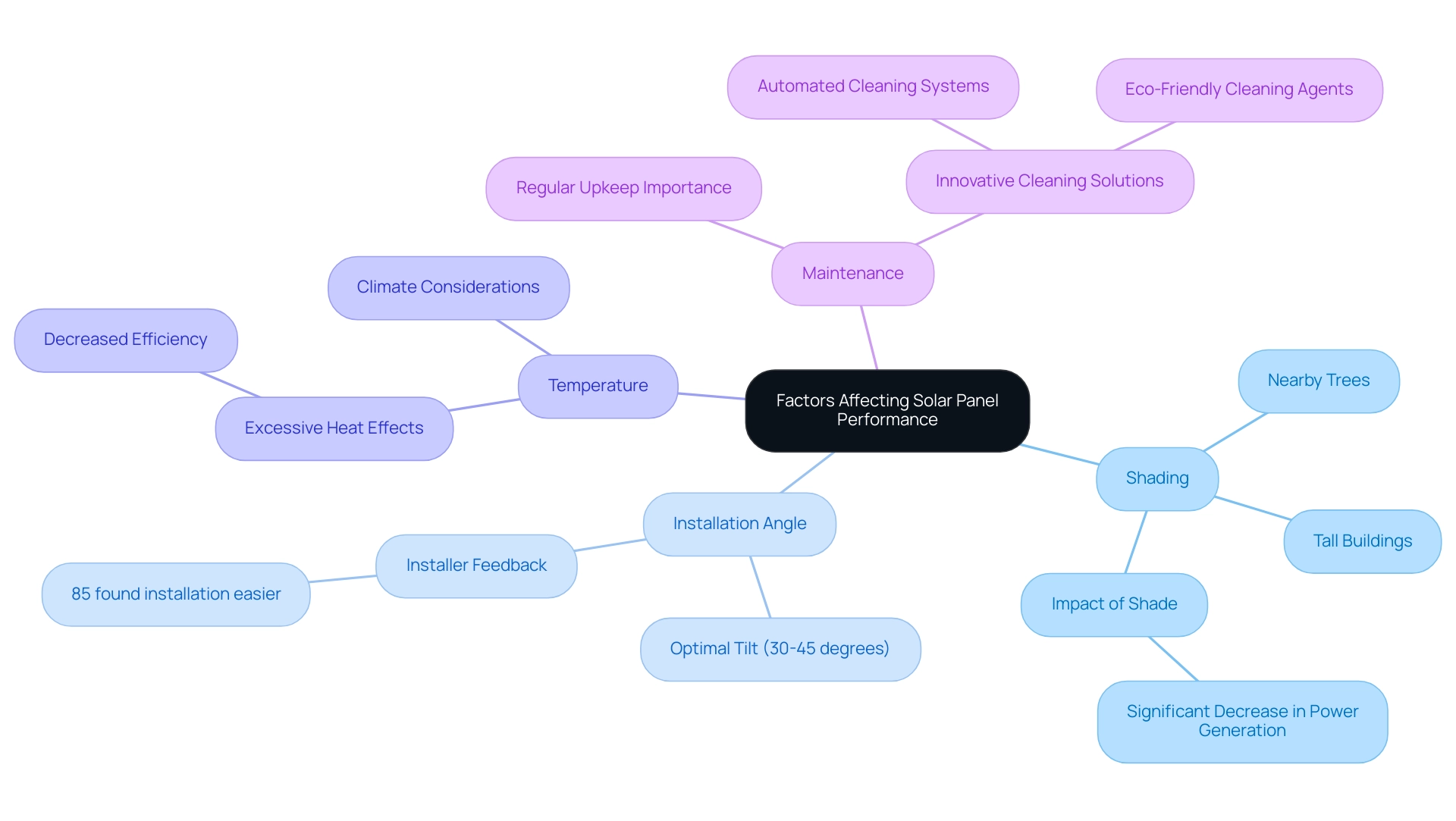
- Shading: One of the most significant culprits in reducing your sunlight output is shading. Whether it’s from nearby trees swaying in the breeze or taller buildings casting shadows, any obstruction can block sunlight and diminish your system’s effectiveness. For example, even a slight amount of shade can result in a significant decrease in power generation.
- Installation Angle: Were you aware that the angle at which your modules are set up can influence how much sunlight they capture? A tilt between 30 to 45 degrees is generally advised to maximize sunlight exposure, enabling your system to capture energy most effectively throughout the day. In fact, 85% of installers using NREL’s SolarAPP+ permitting software found the installation process significantly easier, which can lead to better installation practices and improved performance.
- Temperature: While photovoltaic modules thrive in sunlight, excessive heat can actually work against them. As temperatures increase, efficiency may decrease, so it’s important to take into account the climate in your area when selecting a photovoltaic system.
- Maintenance: Just like any other investment, regular upkeep is crucial. Maintaining cleanliness and checking for any wear and tear can help sustain optimal performance levels, ensuring you get the most value for your investment. Innovative cleaning solutions, such as automated cleaning systems or eco-friendly cleaning agents, are emerging that can make this task easier, contributing to the longevity and efficiency of your energy investment.
Understanding these factors is vital for homeowners who want to maximize their energy investment. As Barry Elad, a tech enthusiast, aptly puts it, ‘My goal is to make complex tech information easy and accessible for everyone.’ By understanding how shading, angle, temperature, and upkeep influence the performance of energy collectors, you can make informed choices that improve your system’s output and lifespan.
Additionally, it’s important to consider the solar panel sizes and wattage when sizing photovoltaic panels as part of your investment. A well-sized system with the right solar panel sizes and wattage not only meets your energy needs but also optimizes performance based on the factors mentioned. With the renewable energy sector projected to see a strong recovery in 2024, with combined additions from major countries expected to account for 75% of global additions, now is the perfect time to dive into these details!
Furthermore, a recent case study titled ‘Future Outlook for the Industry’ revealed that despite challenges in 2023, 34% of companies expect growth in 2024, suggesting a positive outlook for investments in renewable energy.
Choosing the Right Solar Panel Size for Your Energy Needs
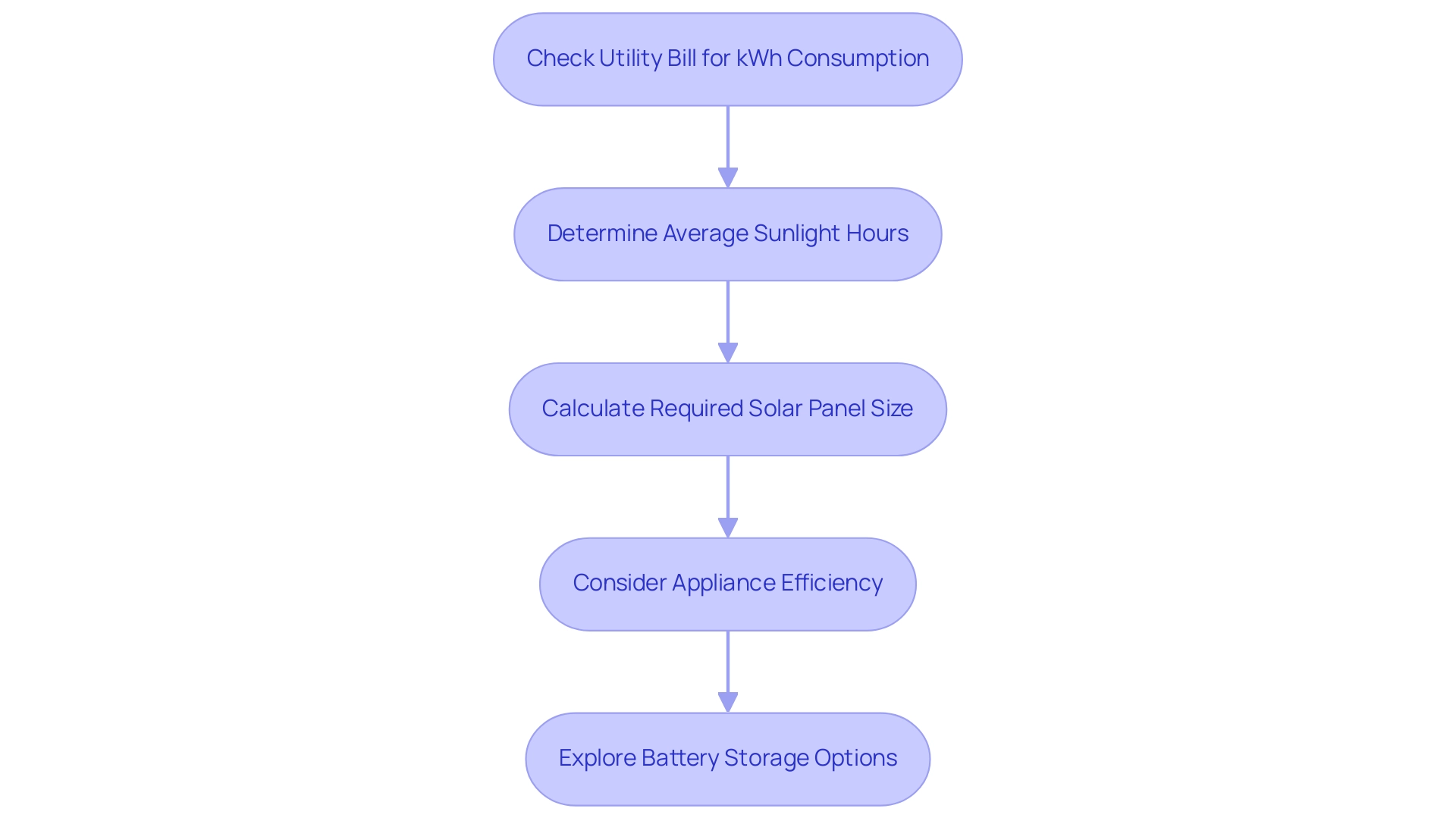
Establishing the appropriate solar panel sizes and wattage to meet your power requirements begins with understanding your average monthly electricity consumption. The first step is to check your utility bill for your kilowatt-hour (kWh) consumption. Once you have that figure, divide it by the average sunlight hours your area receives—this is crucial for determining how many units will do the job.
For instance, if your monthly usage is around 600 kWh and you enjoy about 5 hours of sunlight each day, you would need approximately 5 solar panel sizes and wattage of 300 watts each to adequately meet your requirements. This simple calculation ensures that your household’s consumption is matched with the appropriate solar panel sizes and wattage. In locations such as Long Beach, where eco-conscious homeowners seek efficient power solutions, being mindful of electricity use is particularly important.
As the US Department of Energy highlights, homes with higher-wattage lamps tend to use more power. Understanding your usage patterns can make a significant difference; for example, using an average dishwasher consumes about 1,800 watts of power per cycle, translating to an average of 1.8 kWh of electricity. Homeowners can benefit from strategies like upgrading to efficient appliances or enhancing insulation to decrease consumption.
Simple actions such as sealing leaks and switching to LED bulbs can significantly reduce utility costs and enhance your home’s overall efficiency and eco-friendliness. Moreover, examining the best battery options for storing power, like lithium-ion batteries or lead-acid batteries, can enhance your investment, guaranteeing you have dependable electricity when you require it the most. Comprehending how photovoltaic cells transform sunlight into electricity is also crucial for property owners aiming to make informed choices regarding their energy systems.
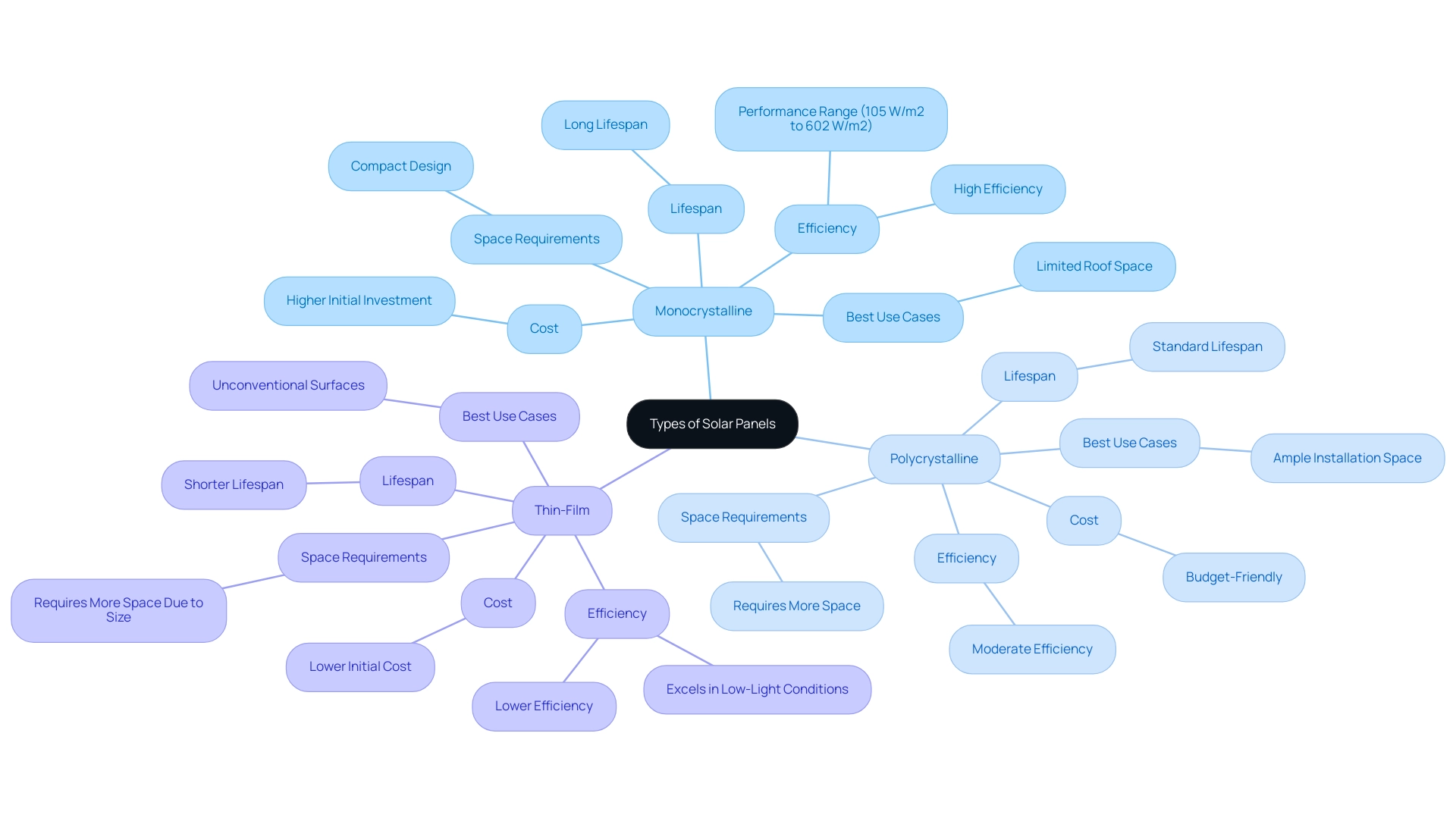
Comparing Different Types of Solar Panels: Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-Film
When it comes to solar panels, homeowners generally consider three main types:
- Monocrystalline: These panels are celebrated for their high efficiency—often the most efficient option available—and their sleek, modern appearance. This makes them a fantastic choice for those with limited roof space. Additionally, monocrystalline modules typically boast a longer lifespan, making them a solid investment in the long run. Their performance can vary with changing irradiance, ranging from 105 W/m2 to 602 W/m2, underscoring their effectiveness in different conditions.
- Polycrystalline: While slightly less efficient than their monocrystalline counterparts, polycrystalline modules offer a more budget-friendly alternative. They’re particularly popular among homeowners with ample installation space. However, it’s worth noting that their multiple silicon crystals can lead to decreased performance in high-temperature situations, which might be a consideration depending on your local climate. As emphasized in the case study ‘Comparison of Solar Cell Types,’ both monocrystalline and polycrystalline units serve the same purpose of converting sunlight into electricity, but they vary in efficiency, cost, and appearance, which can affect your choice.
- Thin-Film: Lightweight and flexible, thin-film structures are ideal for unconventional surfaces, such as curved roofs or building-integrated designs. Despite their lower efficiency compared to the other types, they excel in low-light conditions, making them a viable option in certain scenarios. However, home installations typically require more space due to their lower solar panel sizes and wattage. Bifacial modules, which employ conductive material on both surfaces to capture reflected sunlight, are another choice, although they necessitate specific installation conditions that can raise expenses.
Along with comprehending these module types, it’s crucial to assess service providers to discover the best value in renewable solutions. As highlighted in the case study “How Property Owners Benefited from Household Solar Systems Under the 200% Rule,” many residents have successfully lowered their power expenses and enhanced their autonomy by selecting the appropriate solar solutions. As an eco-aware property owner, think about how these systems can integrate into the larger framework of your power requirements and budgets, including choices for residential EV charging stations.
Each panel type presents unique advantages and disadvantages, so understanding the differences in solar panel sizes and wattage is essential for selecting the best fit for your specific needs.
Moreover, the “200% Rule” enables homeowners to size their systems to generate sufficient power to meet their electric requirements and potentially reduce some of their consumption through net metering. As Jacob Marsh wisely puts it,
Your decision comes down to your personal preferences, space constraints, and financing options.
This guidance is invaluable as you navigate the exciting journey of solar energy for your home.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of solar panels is vital for homeowners looking to make a sustainable choice for their energy needs. From the various standard sizes and dimensions that accommodate different roofing configurations to the importance of wattage in determining energy output, each aspect plays a significant role in optimizing solar energy systems. The decision between monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels also influences both efficiency and cost, making it essential to choose wisely based on individual requirements.
Several factors, such as shading, installation angle, temperature, and maintenance, can greatly affect solar panel performance. By recognizing these elements, homeowners can maximize their investment and ensure that their solar systems operate efficiently. Additionally, understanding one’s energy consumption patterns helps in selecting the right number of panels, ensuring that the system is tailored to meet household needs effectively.
As the demand for solar energy continues to rise, embracing this clean energy solution not only contributes to significant savings on utility bills but also supports a healthier planet. By making informed choices about solar panel types, sizes, and installation practices, homeowners can confidently embark on their journey towards energy independence and sustainability. The future of solar energy is bright, and now is the perfect time to harness its potential for a greener tomorrow.