Introduction
As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to gain popularity, understanding the charging options available becomes increasingly important for drivers. Among these options, Level 3 chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, stand out for their ability to recharge an EV’s battery in a fraction of the time compared to standard chargers. This rapid charging capability is transforming the way people think about electric mobility, making long-distance travel more feasible and convenient.
With governments around the world investing in charging infrastructure and technological advancements paving the way for a sustainable future, homeowners are now faced with the exciting potential of installing Level 3 chargers at home. However, the decision comes with its own set of considerations, from installation costs to compatibility with various vehicle models.
This article explores the ins and outs of Level 3 charging, helping homeowners navigate the opportunities and challenges that come with this innovative technology.
What is a Level 3 Charger and How Does It Work?
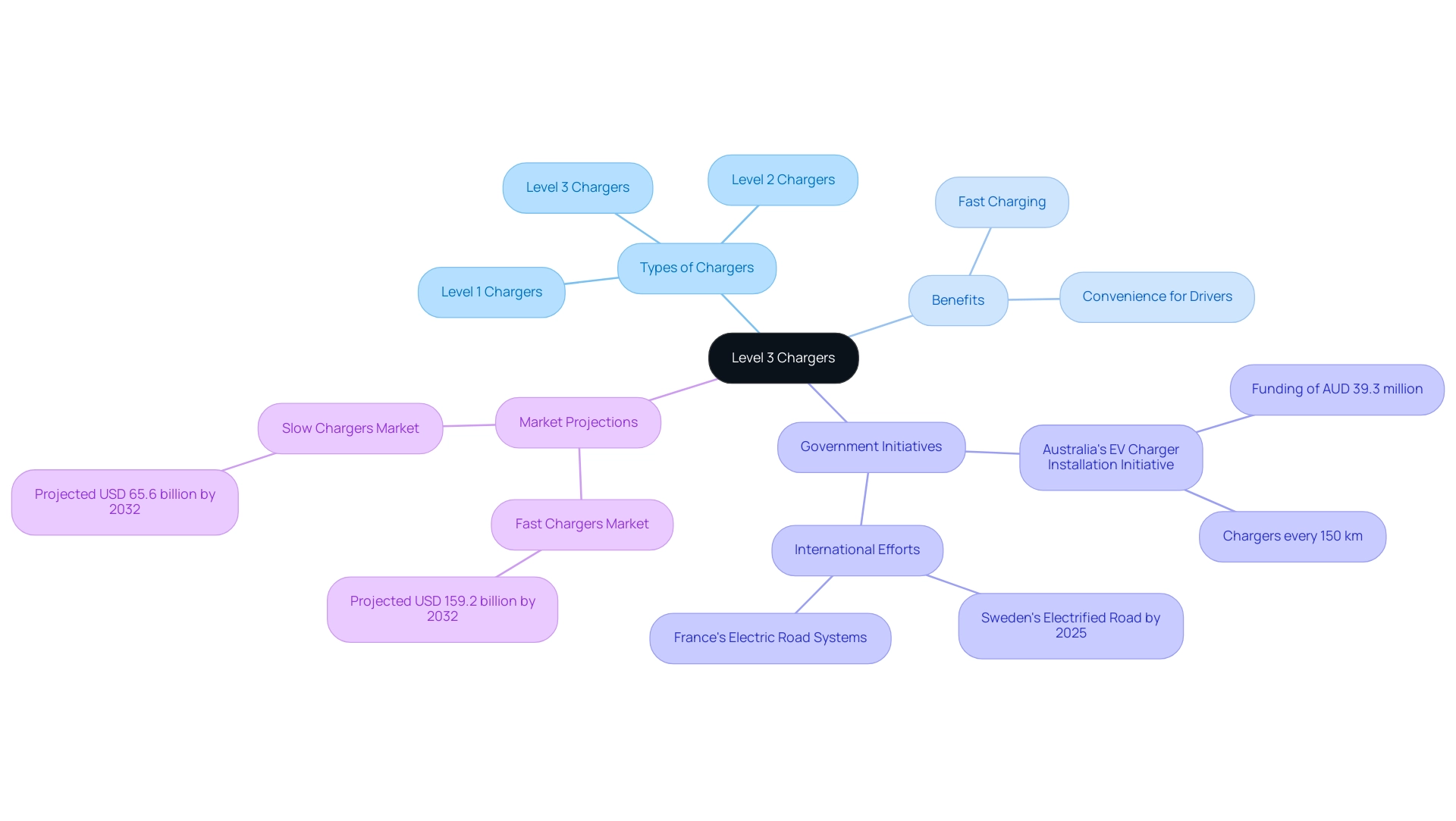
A Type 3 power source, frequently called a DC fast station, is a game changer for electric vehicle (EV) owners. In contrast to the more prevalent Level 1 or Level 2 devices, which offer slower power options, Level 3 units utilize direct current (DC) to greatly accelerate the process. They convert AC power from the grid into DC power, allowing an EV’s battery to charge from 0% to 80% in approximately 30 minutes.
This rapid refueling capability is especially beneficial for drivers who find themselves on the go and need a quick power boost. As these devices become increasingly available in urban areas and along highways, they are playing a crucial role in the evolving landscape of EV charging infrastructure. The Australian Government has acknowledged the significance of enhancing this infrastructure, declaring in 2023 a funding of AUD 39.3 million to the National Roads and Motorists’ Association to construct EV stations along national highways.
This initiative aims to install charging stations every 150 km, enhancing connectivity for EV users. Furthermore, nations such as Sweden and France are developing powered road systems to reduce emissions from freight, with Sweden pledging to a permanently electrified route by 2025. With the global market for rapid charging devices projected to reach around USD 159.2 billion by 2032, it’s clear that DC fast charging technology is paving the way for a sustainable and efficient future in electric mobility.
Installing a Level 3 Charger at Home: Costs and Requirements
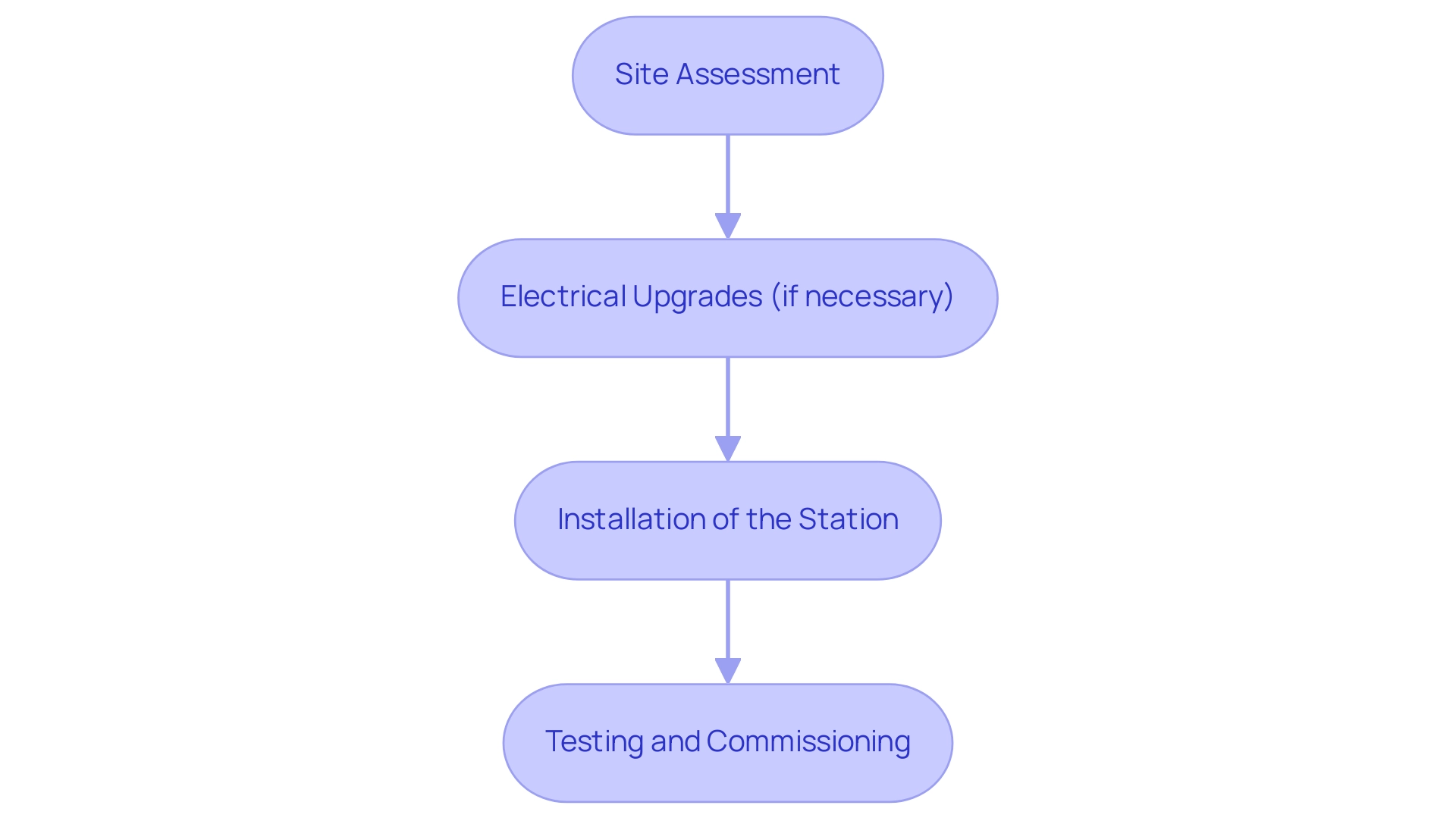
When considering the installation of an at home level 3 charger, it’s essential to understand the comprehensive process involved. At Powercore Electric, we start with a comprehensive site evaluation to identify the optimal placement for your charging station and evaluate any required electrical enhancements. This includes evaluating your home’s electrical infrastructure to ensure it can handle the high power demands of these chargers, which might involve upgrading your electrical panel or wiring.
The installation process typically follows these steps:
- Site Assessment: A detailed evaluation of your property.
- Electrical Upgrades (if necessary): Modifications to your existing electrical system.
- Installation of the Station: Setting up the EV power supply station to comply with all safety and regulatory standards.
- Testing and Commissioning: Rigorous testing to ensure optimal functionality before handover.
Installation costs typically range from $5,000 to $10,000, depending on the complexity and local labor rates.
As one electrician wisely noted, ‘Proper planning and installation not only ensure safety but also maximize the efficiency of your power setup.’ Consulting with a licensed electrician can help you navigate these requirements and provide tailored recommendations. Don’t forget to explore local regulations and potential incentives; many regions offer rebates or tax credits that can significantly offset installation costs.
For instance, federal tax credits of up to $1,000 can mitigate initial expenses, making this a practical choice for eco-conscious homeowners. With manufacturers estimating that drivers should anticipate at least 10 years or 100,000 miles from a battery-powered vehicle, investing in a Type 3 charger is a wise choice. By being informed about these aspects, you can make the most of your investment in electric vehicle refueling.
Pros and Cons of Level 3 Charging: Is It Right for You?
Level 3 charging offers several compelling advantages, chief among them being the significantly reduced charging times. For those who find themselves in need of a quick charge—perhaps during a long road trip or a busy day—these devices can be a game changer. They enhance the overall convenience of electric vehicle ownership, particularly for drivers who cover extensive distances regularly.
In fact, recent studies indicate that by 2035, the share of electricity from devices other than home units is predicted to reach nearly 45%, showcasing the growing reliance on rapid options as EV technology continues to evolve.
Moreover, the Australian Government has committed AUD 39.3 million to support the installation of EV stations along national highways, demonstrating a strong governmental push towards enhancing infrastructure. Additionally, the recent case study on the UK public network reveals that in 2024, 4,353 rapid or ultra-rapid charge points were added, marking a 28% increase from 2023. This trend highlights the growing accessibility of third-tier charging stations, which could greatly assist electric vehicle owners.
Nonetheless, it’s essential to take into account the drawbacks. The installation of an at home level 3 charger can be quite costly, and not every home may have the necessary electrical infrastructure to support such a charger. This indicates that some homeowners may encounter extra costs beyond merely the at home level 3 charger itself.
Plus, frequent use of these high-powered chargers can result in higher electricity bills—something to factor into your decision-making process.
As you weigh these pros and cons, it’s crucial to reflect on your driving habits and energy needs. For instance, while Level 3 power supply can be incredibly beneficial for those on the go, it may not be the most suitable choice for every EV owner. Real-world experiences from fellow drivers can provide insight on this; many express satisfaction with the convenience of quick replenishment, yet some caution against the costs associated with regular use.
Furthermore, global initiatives like India’s FAME II, which requires stations every 25 km along major highways, highlight the worldwide commitment to enhancing charging infrastructure. Ultimately, it’s about finding the right balance that works for your lifestyle.
Understanding Connector Types and Compatibility for Level 3 Chargers
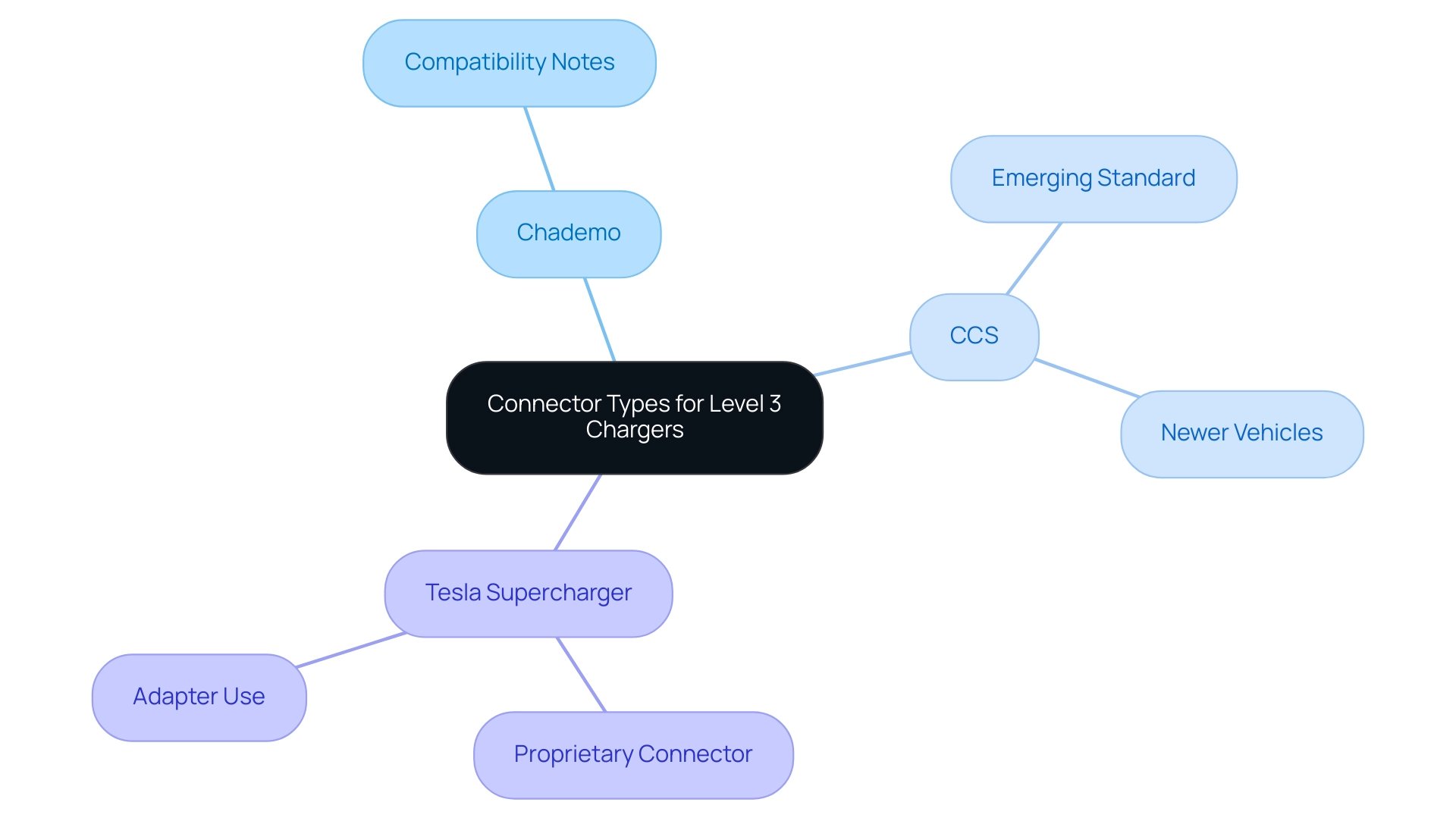
When it comes to Level 3 chargers, it’s essential to be aware of the different connector types available, including:
- Chademo
- CCS (Combined Charging System)
- Tesla Supercharger connectors
Understanding which connector your vehicle supports is crucial to avoid any compatibility hiccups. As we look toward 2024, it’s noteworthy that nearly all newer battery-operated vehicles are being equipped with CCS connectors, positioning them as the emerging standard in the industry.
Meanwhile, Tesla vehicles utilize their proprietary connector but can easily adapt to other types with the right adapter. As Mathilde Carlier, a research expert in transportation and logistics, highlights, the significance of choosing the appropriate power source cannot be exaggerated, especially as TCO parity between battery-powered and ICE vehicles could be achieved in less than 7 years in major EV markets. This emphasizes the increasing importance of efficient power supply infrastructure.
To further demonstrate industry commitment, the EV100 Initiative highlights how 130 global members are devoted to adopting battery-powered vehicles and improving power supply infrastructure by 2030. To maximize your power supply experience, always verify the connector type before buying a Type 3 device. With vehicle sales anticipated to increase by 20% this year—resulting in nearly half a million additional sales—being well-informed about EV power options is more crucial than ever.
Electricity Costs and Savings: What to Expect with Level 3 Charging
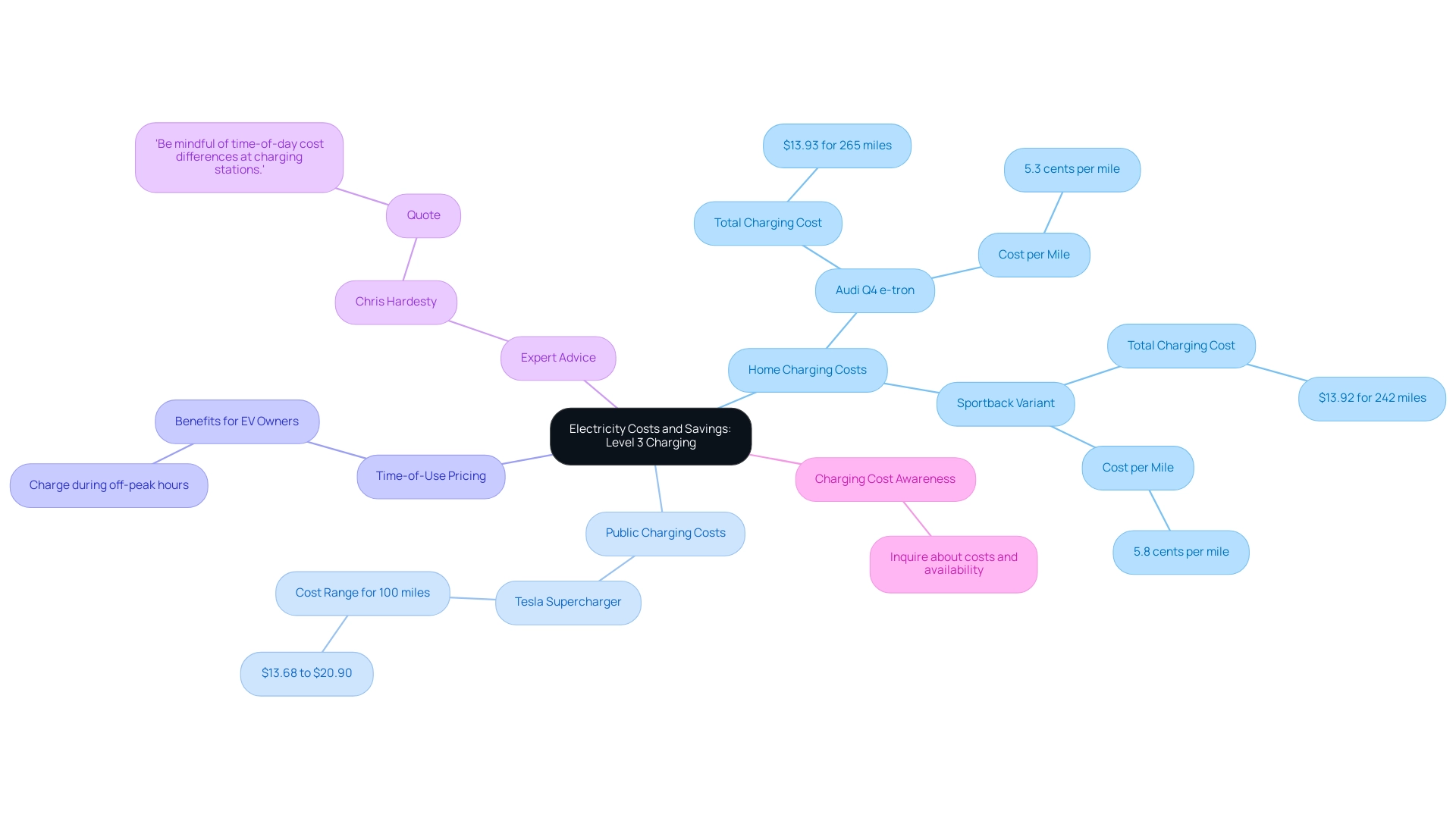
Charging your electric vehicle with a Type 3 charger can significantly affect your electricity costs, with current rates typically fluctuating between $0.20 and $0.60 per kWh based on local utility pricing. While it might seem that home refueling is pricier at first glance, many EV owners quickly realize that the speed and convenience of an at home level 3 charger can outweigh these costs, particularly for those who often take long trips. For instance, the Audi Q4 e-tron, which features an 86 kWh battery, incurs a cost of about $13.93 to reach a range of 265 miles, translating to a mere 5.3 cents per mile.
Meanwhile, the Sportback variant costs $13.92 for 242 miles, equating to 5.8 cents per mile. In comparison, replenishing at a Tesla Supercharger ranges from $13.68 to $20.90 for 100 miles, which can provide a broader context for understanding refueling expenses. Moreover, savvy homeowners can benefit from time-of-use pricing offered by some utility companies, allowing them to charge during off-peak hours when rates are lower.
As Chris Hardesty, senior advice editor, observes, ‘Be mindful of time-of-day cost differences at power stations.’ By evaluating these rates and potential savings, including inquiring about charging costs and availability at public stations, EV owners can maximize their Level 3 charging experience with an at home level 3 charger and enjoy the convenience of electric travel without breaking the bank.
Conclusion
Level 3 chargers are revolutionizing the electric vehicle landscape by offering rapid charging capabilities that make long-distance travel more practical and convenient. With the ability to charge an EV’s battery from 0% to 80% in just around 30 minutes, these chargers are becoming essential for those who are always on the go. As governments worldwide invest in expanding charging infrastructure, the push towards adopting Level 3 chargers at home is gaining momentum, providing homeowners with an opportunity to enhance their electric mobility experience.
However, the decision to install a Level 3 charger at home involves careful consideration of various factors, including installation costs, necessary electrical upgrades, and compatibility with different vehicle models. While the initial investment may seem significant, potential tax credits and rebates can help mitigate costs, making it a more accessible option for eco-conscious homeowners. It’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons, reflecting on personal driving habits and energy needs to determine if this charging solution aligns with individual lifestyles.
Understanding the different connector types and potential electricity costs associated with Level 3 charging is equally important. As the market for electric vehicles continues to grow, being informed about charging options will empower homeowners to make smart decisions. By embracing this innovative technology, drivers can not only enjoy the convenience of fast charging but also contribute to a more sustainable future. Ultimately, the journey towards electric mobility is about finding the right balance that fits one’s needs while embracing the benefits of a greener lifestyle.