Overview
To determine how big of a solar system you need, start by analyzing your energy consumption patterns from utility bills, accounting for seasonal variations and peak power demands. The article emphasizes that accurately assessing your average monthly usage, considering future energy needs, and understanding peak sun hours are crucial steps in sizing your solar system effectively, ensuring both efficiency and economic viability.
Introduction
In the quest for sustainable living, harnessing solar energy has emerged as a pivotal solution for homeowners aiming to reduce their carbon footprint and energy costs. However, the journey toward an efficient solar system begins with a thorough understanding of one’s energy needs. By analyzing utility bills, recognizing seasonal consumption patterns, and assessing peak sun hours, homeowners can make informed decisions on the size and type of solar system that best fits their lifestyle.
As the demand for renewable energy grows, so do the options available—ranging from advanced solar panels to efficient energy storage solutions. This guide delves into the essential steps for sizing a solar system effectively, ensuring that households not only meet their current energy demands but are also prepared for future needs in a rapidly evolving energy landscape.
Understanding Your Energy Needs: The First Step in Solar Sizing
To find out how big of a solar system do I need for my home, start by analyzing your utility bills from the past year. Concentrate on the total kilowatt-hours (kWh) used each month; this information provides you a thorough understanding of your consumption patterns. Seasonal variations play a significant role in power usage, with factors like space heating contributing approximately 12% to total consumption, particularly during colder months.
Recognizing these variations is essential for sizing your energy setup accurately. Furthermore, comprehending your peak power demands—whether during the day or at night—will significantly impact your solar system selection. As noted, residential households represent approximately 11.8% of total power consumption in the U.S., highlighting the significance of precisely evaluating your requirements.
Investigating available government programs, such as the Home Assistance Program (HEAP), can offer financial support, especially as utility bills can be a considerable burden. Additionally, think about cleaning services for photovoltaic surfaces to maintain efficiency and extend their lifespan. By carefully evaluating your power requirements and considering the latest solar solutions, including:
- Tesla home chargers
- Efficient battery options for residential storage
as well as understanding how solar panels function and the best practices for selecting solar panel inverters, you can answer the question of how big of a solar system do I need to avoid the pitfalls of oversizing or undersizing.
This guarantees you attain both economic savings and long-term sustainability in your consumption.
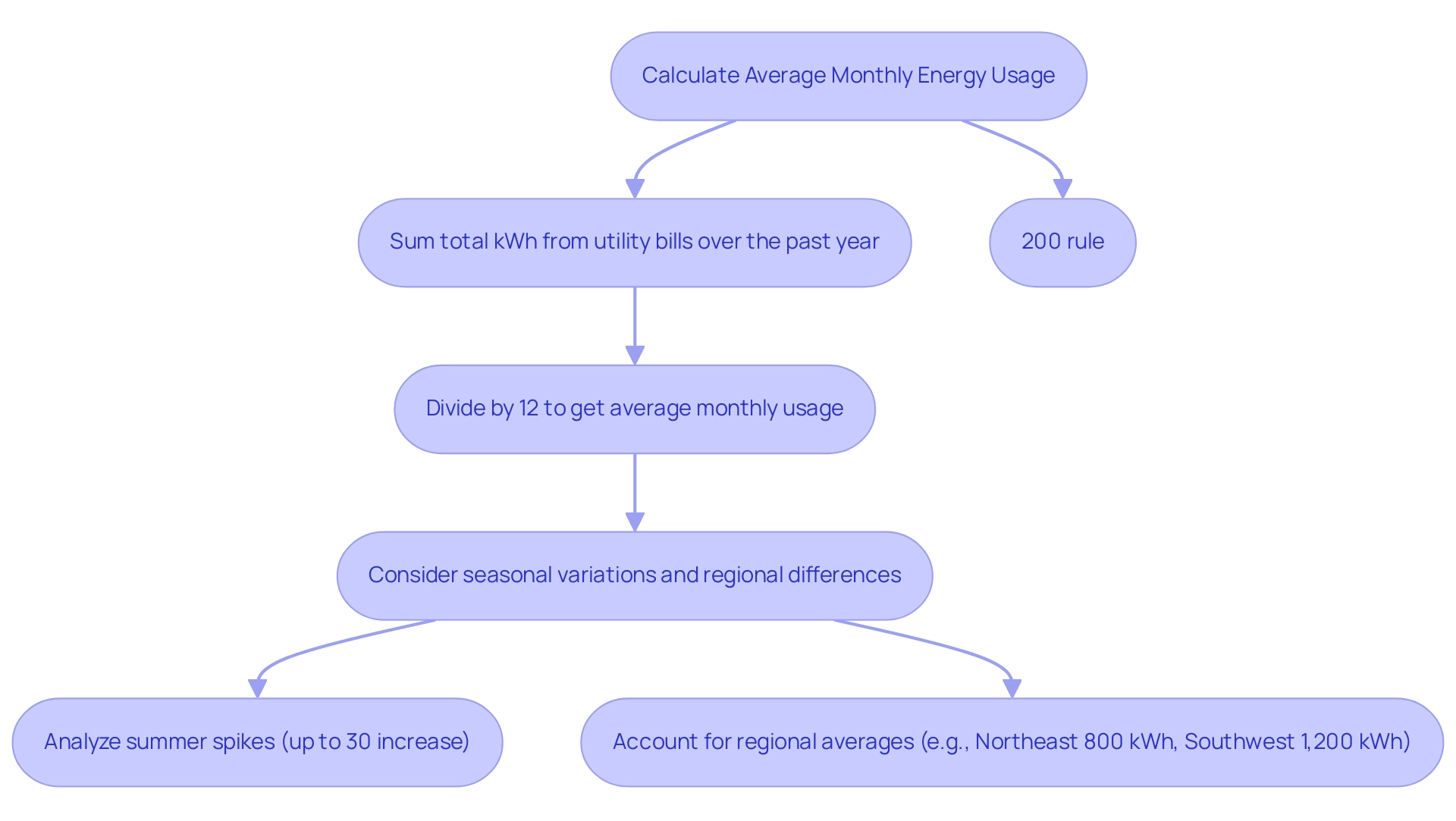
Calculating Your Average Monthly Energy Usage
To accurately determine your average monthly power usage, start by summing the total kilowatt-hours (kWh) from your utility bills over the past year. Divide that figure by 12 to obtain your average monthly usage. For example, if your total annual power consumption amounts to 12,000 kWh, your average monthly usage would be 1,000 kWh.
It’s significant to recognize that power usage can fluctuate with the seasons; hence, it may be wise to estimate how big of a solar system do I need by using the highest average month as a cautious measure, particularly if you expect to enlarge your renewable system in the future. Recent statistics indicate that average monthly power usage can differ significantly by region; for instance:
- Households in the Northeast may average around 800 kWh per month.
- Households in the Southwest may exceed 1,200 kWh.
Understanding these regional differences is crucial for tailoring your calculations.
Furthermore, specialists recommend that comprehending seasonal variations—such as heightened power demand during summer months—can further enhance your sizing calculations. As noted by an analyst, ‘The summer months typically see a spike in consumption due to air conditioning use, which can increase monthly usage by as much as 30% in some areas.’ By examining your energy usage trends and taking into account these variations, along with insights from case studies that demonstrate how various households have gained advantages from photovoltaic installations under the 200% rule, you’ll be better prepared to answer the question of how big of a solar system do I need to fulfill your requirements efficiently.
For instance, one case study highlighted a family that optimized their energy installation by adhering to the 200% rule, resulting in significant savings on their utility bills. Moreover, taking into account the kind of heater—whether active or passive—can additionally improve your setup’s efficiency. Active systems are ideal for consistent heating requirements, while passive systems can be simpler and more cost-effective, especially in regions with abundant sunlight.
By considering these factors, including the 200% rule and case study insights, you can choose a solution that not only aligns with your energy needs and budget but also contributes to a sustainable and eco-friendly home.
Assessing Peak Sun Hours: A Key Factor in Solar Production
Peak sun hours are described as the times when sunlight is strong enough to allow photovoltaic systems to function at optimal efficiency. To assess the peak sun hours in your area, it’s advantageous to refer to maps or local climate data. For instance, regions in California typically experience between 4 to 7 peak sun hours daily, while New Mexico shows a range of 6 to 7 hours.
It’s crucial to recognize that in regions with fewer peak sun hours, technologies such as bifacial modules can improve efficiency by capturing reflected light, making renewable sources viable even in less sunny areas. This emphasizes the comparative performance of photovoltaic technologies and their adaptability. For example, if your location averages 5 peak sun hours per day, you can calculate your monthly peak sun hours by multiplying this figure by 30, resulting in a total of 150 hours.
This calculation is essential, as it directly affects the energy production capacity of your photovoltaic devices, thereby determining the ideal size of the energy system to sufficiently satisfy your energy requirements. Additionally, positioning photovoltaic panels at an angle that maximizes exposure to sunlight is crucial; typically, an angle equal to your latitude plus 15 degrees is recommended for optimal performance. Experts from Sungold emphasize, ‘Modern technology related to sunlight is getting more efficient, making it viable in more places,’ underscoring the advancements in energy solutions.
Furthermore, choosing the appropriate battery is crucial for effective power storage. Options like lithium-ion batteries provide excellent performance and longevity. Unbound Solar offers a peak sun hours map and additional insolation data, helping eco-aware homeowners choose the optimal inverter and assess their renewable power needs efficiently.
Choosing the Right Solar Panels: Types and Efficiencies
When evaluating how big of a solar system do I need for your home, it’s essential to assess the efficiency ratings of the solar devices, which typically range from 15% to 22%. Higher efficiency systems not only generate more energy within a smaller footprint but also significantly reduce utility costs, enhance energy independence, and promote sustainability. For instance, if your goal is to produce 1,000 kWh per month, understanding how big of a solar system do I need with a module that has 20% efficiency means you’ll require fewer units compared to one rated at 15% efficiency—potentially saving both installation costs and space.
In fact, to determine how big of a solar system do I need, one could consider that 17-30 400-watt units could power an average U.S. home, emphasizing the importance of efficiency in your selection process.
Consider the different types of solar panels available:
- Monocrystalline panels are known for their high efficiency (typically 15-22%) and longevity, making them a popular choice despite their higher cost.
- Polycrystalline modules tend to be more affordable but usually offer slightly lower efficiency (around 13-16%).
- Thin-film modules are lightweight and flexible, ideal for certain applications, but they generally provide the lowest efficiency (around 10-13%).
Additionally, it’s important to examine the warranty and lifespan of each type, as these factors significantly affect long-term performance and cost savings. As Jason Svarc, a certified expert in energy systems and batteries, observes, ‘A high-efficiency 400W+ module could cost $350 or more, while a common 370W unit will typically cost closer to $185.’ This highlights the importance of considering both upfront costs and potential energy savings when making your selection.
Moreover, a comparative study of energy systems in Massachusetts demonstrated how investing in higher efficiency units can result in increased electricity generation, addressing the question of how big of a solar system do I need to validate the greater initial expenditure. For a more comprehensive understanding of pricing, homeowners should consider tiered pricing models across different brands and types of products, as well as potential rebates and incentives that can further affect overall costs. By utilizing resources like the EnergySage Marketplace, eco-conscious homeowners can effectively compare photovoltaic panels based on efficiency, power output, warranty, and price to make informed decisions tailored to their power requirements, ensuring they choose the best options available in a growing industry that employed over 263,000 workers in the U.S. as of December 2022.
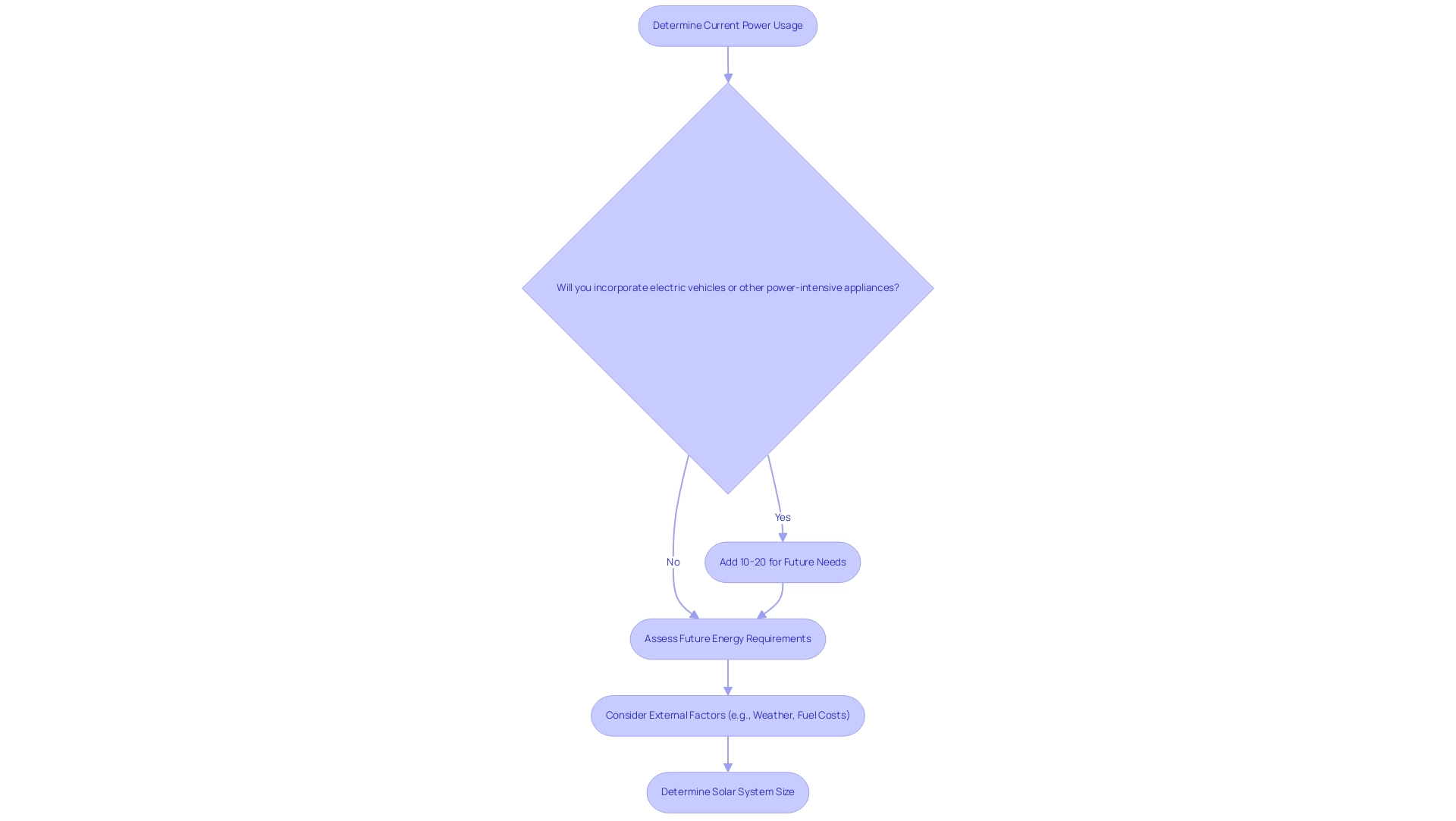
Planning for the Future: Anticipating Energy Needs and System Expansion
When determining how big of a solar system do I need, it’s crucial to consider not just your current power usage but also your future power requirements, especially if you intend to incorporate electric vehicles into your lifestyle. Alterations such as the inclusion of electric vehicles, home expansions, or new power-intensive appliances can significantly influence your household’s power requirements. Experts suggest preparing for these possible increases by adding 10-20% to your projected power requirements.
This proactive approach protects against the risk of under-sizing your system, ensuring it remains efficient and capable of meeting your power demands as they grow, particularly in a world increasingly reliant on sustainable driving solutions.
The recent extreme weather events that caused major power outages in the U.S. and India in 2023 highlight the critical need for resilience in system design. By anticipating future power requirements, you can figure out how big of a solar system do I need to avoid costly upgrades or additional installations, thereby enhancing both the resilience and efficiency of your solar setup. Furthermore, with U.S. hydropower generation anticipated to rise by 6% in 2024, understanding broader power trends is essential.
The variability in power demand, influenced by unpredictable weather conditions and fuel costs—as illustrated in the case study on electricity forecasts—emphasizes the importance of planning for future needs. With the rising trends in power usage, particularly from electric vehicles, and the difficulties presented by severe weather occurrences, such foresight is vital for long-term sustainability and reliability in your power supply.
Additionally, incorporating Tesla home chargers can offer a seamless solution for electric vehicle owners, ensuring that your photovoltaic system can accommodate the additional power demands. Homeowners should also investigate available government initiatives that encourage the adoption of renewable power, which can significantly lower initial expenses and improve the economic feasibility of such investments. Understanding the economic advantages of solar energy solutions not only aids in decision-making but also contributes to a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Understanding your energy needs is the cornerstone of effectively sizing a solar system. By analyzing utility bills, seasonal consumption patterns, and peak energy demands, homeowners can make informed decisions that align with their current and future energy requirements. The importance of accurately assessing energy consumption cannot be overstated, as it lays the groundwork for optimizing solar panel selection and enhancing energy efficiency.
Calculating average monthly energy usage and recognizing regional differences in consumption are essential steps in this process. Seasonal fluctuations can significantly impact energy needs, making it crucial to account for these variations when designing a solar system. Additionally, assessing peak sun hours allows homeowners to maximize the efficiency of their solar panels, ensuring that they generate enough energy to meet their demands.
Choosing the right solar panels based on efficiency ratings and understanding the different types available further contributes to making a sound investment. Higher efficiency panels not only save space but also reduce long-term costs, adding to the economic viability of solar energy solutions.
Finally, planning for future energy needs is vital in an ever-evolving energy landscape. By anticipating changes such as the addition of electric vehicles or new appliances, homeowners can safeguard against under-sizing their system and enhance its resilience against unexpected demands or extreme weather events.
In conclusion, the transition to solar energy represents a significant step toward sustainable living, making it imperative for homeowners to educate themselves on the various factors that influence solar system sizing. By taking these considerations into account, households can achieve both economic savings and a robust, eco-friendly energy solution that meets their needs today and in the future.